目录:
1、前言
2、背景
3、组件效果展示
4、sample解析
5、library解析
6、《鸿蒙开源第三方组件》系列文章合集
<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">前言</span>
基于安卓平台的连续滚动图像组件ContinuousScrollableImageView(https://github.com/Cutta/Cont...)
实现了鸿蒙化迁移和重构,代码已经开源到(https://gitee.com/isrc\_ohos/continuous-scrollable-image-view\_ohos)
欢迎各位开发者下载使用并提出宝贵意见!
<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">背景</span>
ContinuousScrollableImageView\_ohos组件通过让图像连续滚动,来实现动画效果。组件支持对图像的滚动效果进行设置,包括:图像源、缩放类型、持续时间和方向等。该组件提供动态的视觉效果,可以用来开发应用的背景等。
<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">组件效果展示</span>
ContinuousScrollableImageView\_ohos组件库中设置了飞机、云、山三种图像:飞机的滚动方向设置为“RIGHT”,向右侧滚动;云和山的滚动方向设置为“LEFT”,向左滚动。三者组合成一幅完整的、具有连续滚动效果的动画图像,如图1所示。
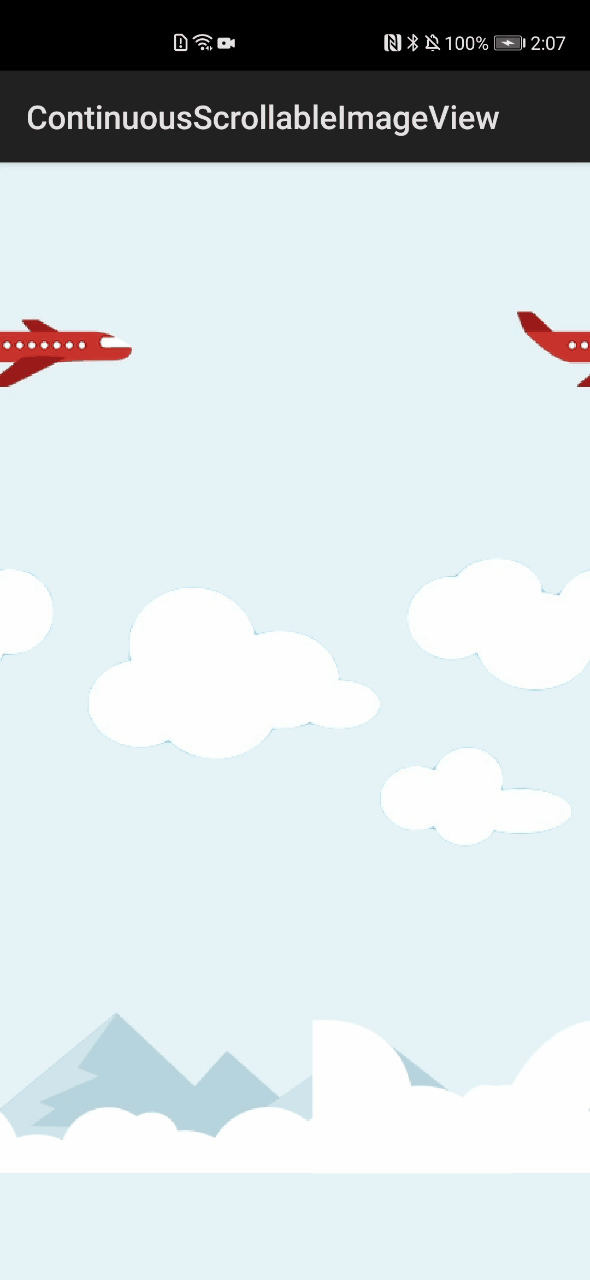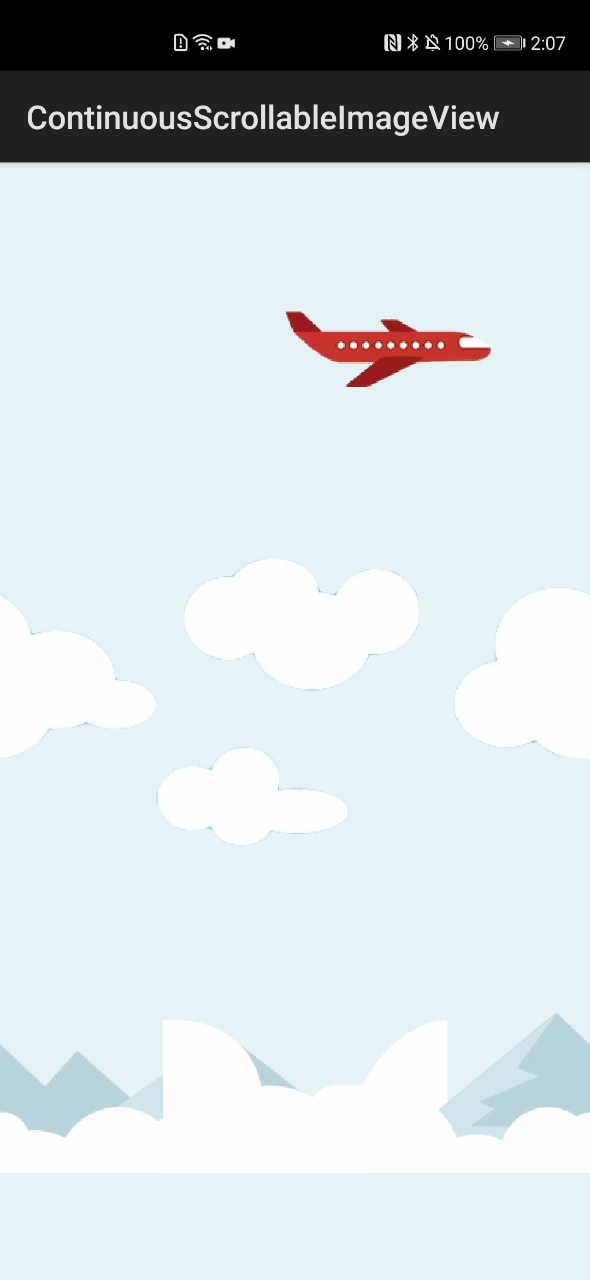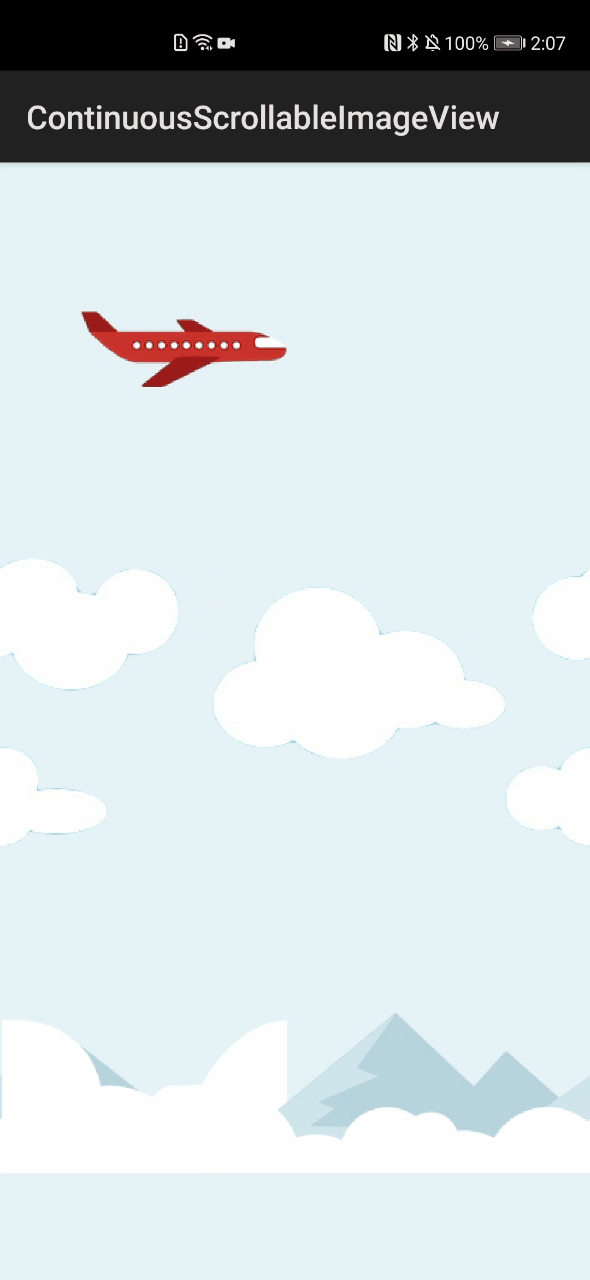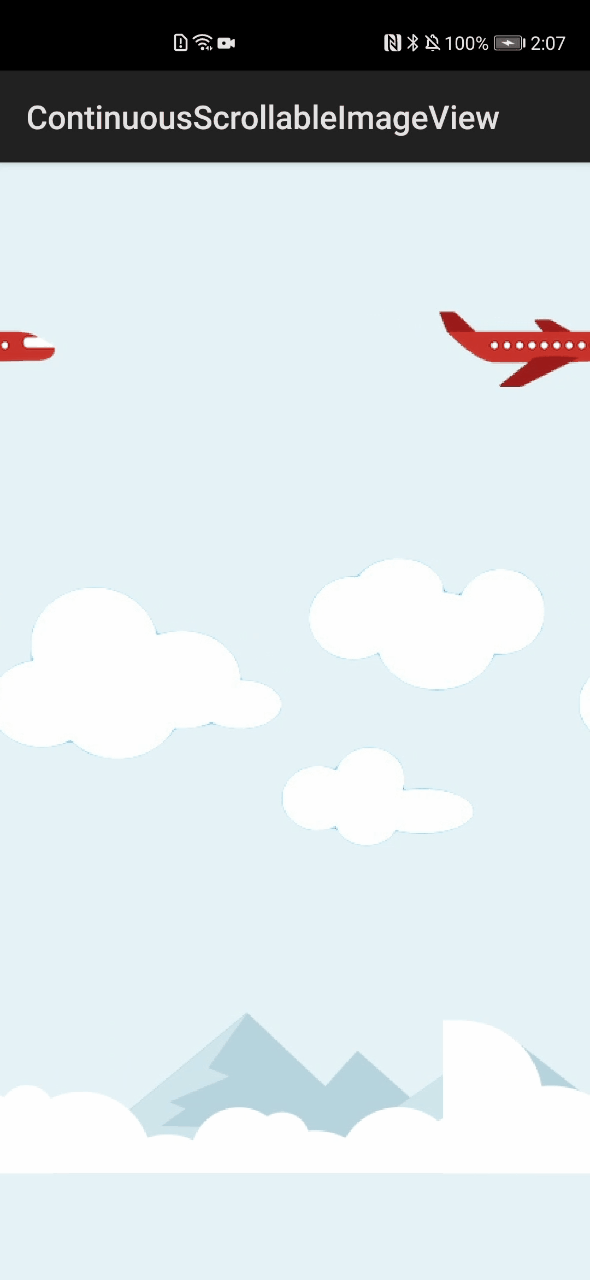
图1 ContinuousScrollableImageView\_ohos组件运行效果图
<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">Sample解析</span>
Sample部分主要负责搭建整体的显示布局,并实例化飞机、云、山三种图像的对象。通过调用Library提供的接口,对三个对象的滚动效果进行属性设置。想要实现图1所示的动画效果,需要以下3个步骤:
步骤1. 导入ContinuousScrollableImageView类。
步骤2. 实例化类对象并设置各个对象的属性。
步骤3. 将对象添加到整体显示布局中。
下面我们来看一下每个步骤涉及的详细操作。
1、导入ContinuousScrollableImageView类
`<span class="token keyword">import</span> com<span class="token punctuation">.</span>cunoraz<span class="token punctuation">.</span>continuousscrollable<span class="token punctuation">.</span>ContinuousScrollableImageView<span class="token punctuation">;</span>`
2、实例化类对象并设置各个对象的属性
图1中的动画效果需要实例化3个ContinuousScrollableImageView对象分别代指包含飞机、云、山三种图像。
设置各对象属性的方式有两种:常用方式和Builder方式。常用方式是指通过对象单独调用类接口的方式;Builder方式即建造者模式。用户可根据个人需要,自行确定使用哪种方式设置对象属性。此处为了证明两种方式的有效性,飞机和云图像采用常用方式设置属性,山图像采用Builder方式设置属性。
ContinuousScrollableImageView对象的可设置属性有4个,包括:滚动方向、滚动周期、缩放类型、图像源。
(1)实例化飞机图像的对象并进行属性设置
<section class="prettyprint"><pre>// 实例化对象</pre>
ContinuousScrollableImageView plane=new ContinuousScrollableImageView(this);
// 采用常用方式进行属性设置
LayoutConfig planeConfig=new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,0,LayoutConfig.UNSPECIFIED_ALIGNMENT,1);
plane.setLayoutConfig(planeConfig);
plane.setDirection(ContinuousScrollableImageView.RIGHT); //设置滚动方向向右
plane.setDuration(2500); //设置滚动周期
plane.setScaleType(ContinuousScrollableImageView.CENTER_INSIDE); //设置缩放类型
plane.setResourceId(ResourceTable.Media_plane); // 设置图像源1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.
</section>
(2)实例化云图像的对象并进行属性设置
// 实例化对象
ContinuousScrollableImageView cloud=new ContinuousScrollableImageView(this);
// 采用常用方法进行属性设置
LayoutConfig cloudConfig=new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,0,LayoutConfig.UNSPECIFIED_ALIGNMENT,1);
cloud.setLayoutConfig(cloudConfig);
cloud.setDirection(ContinuousScrollableImageView.LEFT); //设置滚动方向向左
cloud.setDuration(4000); //设置滚动周期
cloud.setResourceId(ResourceTable.Media_cloud); //设置图像源(3)实例化山图像的对象并进行属性设置
LayoutConfig mountainConfig=new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,0,LayoutConfig.UNSPECIFIED_ALIGNMENT,1);
//采用Builder方式进行对象创建和属性设置
ContinuousScrollableImageView mountain=new ContinuousScrollableImageView.Builder(this.getAbility())
.setDirection(ContinuousScrollableImageView.LEFT) //设置方向向左
.setDuration(6000) //设置时间间隔
.setResourceId(ResourceTable.Media_mountain) //设置图像源
.build();
mountain.setLayoutConfig(mountainConfig);
3、对象添加到整体显示布局中
layout.addComponent(cloud); //飞机对象添加到布局
layout.addComponent(mountain); //云对象添加到布局
layout.addComponent(mountain); //山对象添加到布局<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">Library解析</span>
Library向开发者提供ContinuousScrollableImageView类对象的启动接口和属性设置接口。以图1的效果为例,通过调用启动接口,可以让飞机、云和山对象开始滚动;通过调用属性设置接口,可以改变上述对象的滚动效果。由Sample部分可知,ContinuousScrollableImageView类对象的属性设置有两种方式,本节将揭示,不同属性设置方式下属性设置接口的功能实现也存在差异。
1、ContinuousScrollableImageView类对象启动接口
该接口的功能实现内容较多,但主要逻辑较为清晰,主要可以分为四个部分:设置布局、创建数值动画、对不同的滚动方向设置监听和启动动画。
(1)设置布局 
图2 两个布局依次出现
如图2所示,画面中所有的ContinuousScrollableImageView类对象都需要具有循环滚动的效果,以飞机为例:飞机滚动至最右侧时,逐渐显示的部分需要在最左侧重新出现。为此,设计了两个布局:firstImage和secondImage,二者布局相同且循环显示,其中一个布局显示另一个布局消失的部分。
private void setImages() {
......
firstImage = (Image) this.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_first_image);
secondImage = (Image) this.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_second_image);
firstImage.setImageAndDecodeBounds(resourceId);
secondImage.setImageAndDecodeBounds(resourceId);
setScaleType(scaleType);
}
(2)创建数值动画
飞机、云和山都是静态的,想让实现滚动效果,需要借助动画类。此处采用的是数值动画的方式,来启动各对象。同时还需要设置动画的循环次数、线性变化、循环周期等属性。
animator.setLoopedCount(AnimatorValue.INFINITE); //动画无限重复
animator.setCurveType(Animator.CurveType.LINEAR); //动画线性变化
animator.setDuration(duration); //动画的持续时间
(3)对不同的滚动方向设置监听
飞机、云和山都可以设置不同的滚动方向,针对不同的方向设置不同的值动画监听,以飞机为例:当飞机横向滚动时,通过设置firstImage和secondImage的横坐标变化,达到二者循环显示的目的。当飞机竖向滚动动,通过设置firstImage和secondImage的坐标变化,达到二者循环显示的目的。
switch (DEFAULT_ASYMPTOTE) {
case HORIZONTAL: // 横向滚动
animator.setValueUpdateListener(new AnimatorValue.ValueUpdateListener() { //值动画监听
@Override
public void onUpdate(AnimatorValue animatorValue, float v) {
// firstImage和secondImage循环显示算法
float progress;
if (DIRECTION_MULTIPLIER == 1)
progress = DIRECTION_MULTIPLIER * (v);
else
progress = DIRECTION_MULTIPLIER * (-v);
float width = DIRECTION_MULTIPLIER * (-firstImage.getWidth());
float translationX = width * progress;
firstImage.setTranslationX(translationX); //设置firstImage的横坐标
secondImage.setTranslationX(translationX - width); //设置secondImage的横坐标
}
});
break;
......
(4)启动动画
动画启动后,飞机、云和山的坐标就会发生变化,此时他们的动画效果就由静态的变成滚动的。
animator.start(); //动画启动2、常用方式下属性设置接口功能实现
飞机和云采用常用方式设置属性,其属性包含:滚动周期、滚动方向、图像源、图像缩放类型。各接口的功能实现较为简单,值得注意的是,在滚动方向和滚动周期功能实现中分别调用了启动接口,此处是为了适应下文即将指出的Builder方式,具体原因将在下文讲述。若开发者只采用常用方式进行属性设置,可以将启动接口从滚动方向和滚动周期功能实现中分离出来,通过飞机或者云的对象单独调用。
//设置滚动周期
public void setDuration(int duration) {
this.duration = duration;
isBuilt = false;
build();
}
//设置方向
public void setDirection(@Directions int direction) {
this.direction = direction;
isBuilt = false;
setDirectionFlags(direction);
build();
}
//设置图像源
public void setResourceId(int resourceId) {
this.resourceId = resourceId;
firstImage.setImageAndDecodeBounds(this.resourceId);
secondImage.setImageAndDecodeBounds(this.resourceId);
}
//设置图像缩放类型
public void setScaleType(@ScaleType int scaleType) {
if (firstImage == null || secondImage == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Image.ScaleMode type = Image.ScaleMode.CENTER;
switch (scaleType) {
···
}
this.scaleType = scaleType;
firstImage.setScaleMode(type);
secondImage.setScaleMode(type);
}
3、Builder方式设置属性
对山采用Builder方式进行属性设置,各属性在功能实现时分别调用了常用方式下的属性设置接口,但是缺少启动接口的调用。
为了在Builder方式下也能正常启动动画,常用方式下的滚动方向和滚动周期功能实现中包含了启动接口,这样当在Builder方式下调用上述接口时,就可以实现动画的启动。
public static final class Builder {
private ContinuousScrollableImageView scrollableImage;
public Builder(Ability ability) {
scrollableImage = new ContinuousScrollableImageView(ability);
}
//设置滚动周期
public Builder setDuration(int duration) {
scrollableImage.setDuration(duration);
return this;
}
//设置图像源
public Builder setResourceId(int resourceId) {
scrollableImage.setResourceId(resourceId);
return this;
}
//设置滚动方向
public Builder setDirection(@Directions int direction) {
scrollableImage.setDirection(direction);
return this;
}
//设置缩放类型
public Builder setScaleType(@ScaleType int scaleType) {
scrollableImage.setScaleType(scaleType);
return this;
}
public ContinuousScrollableImageView build() {
return scrollableImage;
}
}
<span class="size" style="font-size:24px">项目贡献人</span>
刘磊 郑森文 朱伟 陈美汝 王佳思 张馨心
作者:朱伟ISRC
想了解更多内容,请访问51CTO和华为合作共建的鸿蒙社区:https://harmonyos.51cto.com



