公众号文章《业界第一个真正意义上开源100 Gbps NIC Corundum介绍》和《揭秘:普通电脑换上Xilinx Alveo U50 100G网卡传文件会有多快?》发出后,得到了很多粉丝的关注,大家纷纷留言询问重现开源工程的详细过程。团队李钊同学详细写了一下具体的实现步骤,具体如下。前面的操作见前文《开源100 Gbps NIC Corundum环境搭建介绍(一)》。
仿真
三、Running test
接上文,梳理了一下具体的仿真流程,现对整个项目的仿真作以介绍:
总的来讲,两种方式:pytest 和 makefile。
pytest方式调用python库cocotb-test的cocotb-test.simulator.run方法,该方法定义了使用何种仿真器的方法;makefile方式是调用python库cocotb中的makefile.sim,该Makefile会根据运行cocotb的命令行中仿真器的类别来调用不同仿真器的makefile,从而执行相关仿真器的编译和仿真操作。
殊途同归,两种方式最终都是在cocotb-test的框架下去启动编译器仿真器(iverilog)对RTL代码进行编译和仿真。
扩展知识:python库介绍,感兴趣的可以去了解cocotb的使用,功能强大并且高效,cocotb是一个基于CO routine的CO simulation TestBench环境,使用Python验证VHDL和SystemVerilog RTL。
cocotb介绍:https://docs.cocotb.org/en/stable/
cocotb git:https://github.com/cocotb/cocotb
cocotb-test:https://github.com/themperek/cocotb-test
1、成功安装tox——更方便快捷的使用pytest
tox是通用的虚拟环境管理和测试命令行工具。tox能够让我们在同一个Host上自定义出多套相互独立且隔离的python环境(tox是openstack社区最基本的测试工具,比如python程序的兼容性、UT等)。它的目标是提供最先进的自动化打包、测试和发布功能。
- 作为持续集成服务器的前端,大大减少测试工作所需时间;
- 检查软件包能否在不同的python版本或解释器下正常安装;
- 在不同的环境中运行测试代码。
个人思考总结:tox方便仿真环境的搭建和移植,它能够维护项目使用多个版本的python,具体按照个人开发环境进行配置,可以修改项目根目录下tox.ini文件指定python版本,便于维护和移植。更为强大的功能还不理解。。。
成功安装tox的开发者:可以使用命令
`
$ cd /path/to/corundum-master
$ tox`
运行仿真。
在tox环境下,所有的测试都可以通过在根目录下运行 tox 来进行。在这种情况下,tox会建立一个python虚拟环境,并在虚拟环境中安装所有的python依赖项。此外,tox将以pytest -n auto的方式运行pytest,因此它将在多个CPU上并行运行测试。
该命令可以一次性仿真项目内部的所有测试例,会在各个测试例的位置生成仿真文件夹sim_build,该文件夹下包含了编译完成的文件xx.vpp(iverilog编译器对代码编译后生成的文件,类似于questasim的compile后生成的文件)和仿真日志。
2、tox未成功,直接使用pytest
所有测试都可以通过在 repo 根目录下运行 pytest 来运行。建议以pytest -n auto的方式运行,在多个CPU上并行运行多个测试。
$ cd /path/to/corundum-master
$ pytest -n auto (多核)
$ pytest (单核)
此种方法使用的时间会比tox多出不少,但效果是一样的。都是使用pytest方式,最终效果和1、成功安装tox——更方便快捷的使用pytest 中一致,也是运行了所有的测试例。
3、运行单个测试组(单模块测试)
刚玉这个项目的开发者对于每个模块都提供了测试文件,如果我们对某个模块功能不理解可以仿真配合学习。
可以通过在子目录下运行pytest来运行测试组。建议以pytest -n auto的方式运行,在多个CPU上并行运行多个测试。
`$ cd /path/to/corundum/fpga/common/tb/rx_hash
$ pytest -n 4Test session starts (platform: linux, Python 3.9.2, pytest 6.2.2, pytest-sugar 0.9.4)
rootdir: /path/to/corundum, configfile: tox.ini
plugins: parallel-0.1.0, cocotb-test-0.2.0, split-0.1.6.dev1+g97d96c2, sugar-0.9.4, xdist-2.2.1, forked-1.3.0, metadata-1.11.0, html-3.1.1, flake8-1.0.7, cov-2.11.1
gw0 [2] / gw1 [2] / gw2 [2] / gw3 [2]
fpga/common/tb/rx_hash/test_rx_hash.py ✓✓ 100% ██████████
Results (27.68s): 2 passed`
如果想要查看仿真波形文件,请在对应模块目录下使用命令
$ WAVES=1 pytest
运行仿真,仿真结束后会在sim_build文件夹下生成对应测试例的波形文件 xx.fst,使用gtkwave即可观察波形。
4、makefile方式
最后,可以通过运行make来运行单个测试。这个方法提供了覆盖参数和启用FST格式的波形转储的能力,可以在gtkwave中查看。
效果会和4中pytest的方式一样,生成波形文件 xx.fst。终端中的打印日志信息也可以保存下来以供查阅。
$ cd /path/to/corundum/fpga/common/tb/rx_hash
$ make WAVES=1
make results.xml
make[1]: Entering directory '/path/to/corundum/fpga/common/tb/rx_hash'
/usr/bin/iverilog -o sim_build/sim.vvp -D COCOTB_SIM=1 -s rx_hash -P rx_hash.DATA_WIDTH=64 -P rx_hash.KEEP_WIDTH=8 -s iverilog_dump -f sim_build/cmds.f -g2012 ../../rtl/rx_hash.v iverilog_dump.v
MODULE=test_rx_hash TESTCASE= TOPLEVEL=rx_hash TOPLEVEL_LANG=verilog \
/usr/bin/vvp -M /home/alex/.local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/cocotb/libs -m libcocotbvpi_icarus sim_build/sim.vvp -fst
-.--ns INFO cocotb.gpi ..mbed/gpi_embed.cpp:76 in set_program_name_in_venv Did not detect Python virtual environment. Using system-wide Python interpreter
-.--ns INFO cocotb.gpi ../gpi/GpiCommon.cpp:99 in gpi_print_registered_impl VPI registered
-.--ns INFO cocotb.gpi ..mbed/gpi_embed.cpp:247 in _embed_sim_init Python interpreter initialized and cocotb loaded!
0.00ns INFO cocotb __init__.py:247 in _initialise_testbench_ Running on Icarus Verilog version 11.0 (stable)
0.00ns INFO cocotb __init__.py:253 in _initialise_testbench_ Running tests with cocotb v1.6.0.dev0 from /home/alex/.local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/cocotb
0.00ns INFO cocotb __init__.py:274 in _initialise_testbench_ Seeding Python random module with 1622183492
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_001
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_002
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_003
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_004
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_005
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_006
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_007
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:127 in __init__ Found test test_rx_hash.run_test_008
0.00ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:477 in _start_test Running test 1/8: run_test_001
0.00ns INFO ...test.run_test_001.0x7f85f23398e0 decorators.py:312 in _advance Starting test: "run_test_001"
Description: Automatically generated test
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:271 in __init__ AXI stream source
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:272 in __init__ cocotbext-axi version 0.1.13
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:273 in __init__ Copyright (c) 2020 Alex Forencich
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:274 in __init__ https://github.com/alexforencich/cocotbext-axi
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:319 in __init__ AXI stream source configuration:
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:320 in __init__ Byte size: 8 bits
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:321 in __init__ Data width: 64 bits (8 bytes)
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:323 in __init__ AXI stream source signals:
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:326 in __init__ tdata width: 64 bits
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:328 in __init__ tdest: not present
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:328 in __init__ tid: not present
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:326 in __init__ tkeep width: 8 bits
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:326 in __init__ tlast width: 1 bits
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:328 in __init__ tready: not present
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:328 in __init__ tuser: not present
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:326 in __init__ tvalid width: 1 bits
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:367 in _handle_reset Reset de-asserted
0.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.m_axis stream.py:154 in _handle_reset Reset de-asserted
FST info: dumpfile rx_hash.fst opened for output.
4.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:357 in _handle_reset Reset asserted
4.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.m_axis stream.py:144 in _handle_reset Reset asserted
12.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:367 in _handle_reset Reset de-asserted
12.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.m_axis stream.py:154 in _handle_reset Reset de-asserted
20.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:502 in _run TX frame: AxiStreamFrame(tdata=bytearray(b'\xda\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5ZQRSTU\x90\x00\x00'), tkeep=None, tid=None, tdest=None, tuser=None, sim_time_start=20000, sim_time_end=None)
28.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:502 in _run TX frame: AxiStreamFrame(tdata=bytearray(b'\xda\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5ZQRSTU\x90\x00\x00\x01'), tkeep=None, tid=None, tdest=None, tuser=None, sim_time_start=28000, sim_time_end=None)
36.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:502 in _run TX frame: AxiStreamFrame(tdata=bytearray(b'\xda\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5ZQRSTU\x90\x00\x00\x01\x02'), tkeep=None, tid=None, tdest=None, tuser=None, sim_time_start=36000, sim_time_end=None)
40.00ns INFO cocotb.tb test_rx_hash.py:191 in run_test RX hash: 0x00000000 (expected: 0x00000000) type: HashType.0 (expected: HashType.0)
48.00ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:502 in _run TX frame: AxiStreamFrame(tdata=bytearray(b'\xda\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5ZQRSTU\x90\x00\x00\x01\x02\x03'), tkeep=None, tid=None, tdest=None, tuser=None, sim_time_start=48000, sim_time_end=None)
48.00ns INFO cocotb.tb test_rx_hash.py:191 in run_test RX hash: 0x00000000 (expected: 0x00000000) type: HashType.0 (expected: HashType.0)
56.00ns INFO cocotb.tb test_rx_hash.py:191 in run_test RX hash: 0x00000000 (expected: 0x00000000) type: HashType.0 (expected: HashType.0)
################ skip a very large number of lines ################
252908.01ns INFO cocotb.rx_hash.s_axis axis.py:502 in _run TX frame: AxiStreamFrame(tdata=bytearray(b'\xda\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5ZQRSTU\x08\x00E\x00\x00V\x00\x8c\x00\x00@\x06d\xfc\n\x01\x00\x8c\n\x02\x00\x8c\x00\x8c\x10\x8c\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00P\x02 \x00mo\x00\x00\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06\x07\x08\t\n\x0b\x0c\r\x0e\x0f\x10\x11\x12\x13\x14\x15\x16\x17\x18\x19\x1a\x1b\x1c\x1d\x1e\x1f !"#$%&\'()*+,-'), tkeep=None, tid=None, tdest=None, tuser=None, sim_time_start=252908007, sim_time_end=None)
253000.01ns INFO cocotb.tb test_rx_hash.py:191 in run_test RX hash: 0x6308c813 (expected: 0x6308c813) type: HashType.TCP|IPV4 (expected: HashType.TCP|IPV4)
253008.01ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:373 in _score_test Test Passed: run_test_008
253008.01ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:496 in _log_test_summary Passed 8 tests (0 skipped)
253008.01ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:569 in _log_test_summary ***********************************************************************************
253008.01ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:586 in _log_sim_summary *************************************************************************************
** ERRORS : 0 **
253008.01ns INFO cocotb.regression regression.py:268 in tear_down Shutting down...
make[1]: Leaving directory '/home/alex/UCSD/Projects/corundum-clean-build/fpga/common/tb/rx_hash'5、总结
包含了一个广泛的基于Python的开源仿真框架,以评估完整设计。该框架使用Python库MyHDL构建,并包括PCI Express系统基础架构,PCI Express硬IP内核,NIC驱动程序和以太网接口的仿真模型。该仿真框架通过提供整个系统状态的可视性,有助于调试完整的NIC设计。
PCIe仿真框架的核心由大约4,500行Python组成,并包括PCIe基础结构组件的事务层模型,其中包括根联合体,功能,端点和交换机以及高级功能,包括配置空间,功能,总线枚举,根联合体 内存分配,中断和其他功能。其他模块由另外4,000行Python组成,提供FPGA PCIe硬IP核的模型,与模拟的PCIe基础设施交换事务层流量,并驱动可连接至共同仿真的Verilog设计的信号。
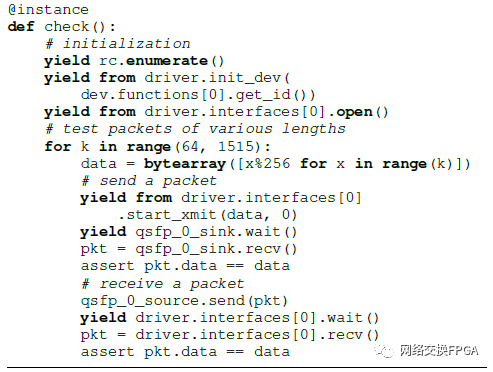
模拟Corundum需要几行代码来实例化和连接所有组件。清单1显示了使用模拟框架发送和接收各种大小的数据包的简化测试台,在Icarus Verilog中共同模拟了Verilog设计。该测试平台实例化了以太网接口端点,PCIe根联合体和驱动程序的仿真模型,并将它们连接到协同仿真的设计。然后,它初始化PCIe基础结构,初始化驱动程序模型,并发送,接收和验证几个不同长度的测试数据包。
清单1. NIC测试台的缩写。包括设置PCIe,以太网接口和驱动程序模型,初始化模拟的PCIe总线和驱动程序以及发送和接收测试数据包。为简洁起见,大多数信号已删除。
无论使用何种方式,只要能成功调用编译器iverilog即可,我们接下来便可搭配产生的波形文件去学习整个工程了!
FPGA工程恢复
以下主要讲述如何恢复VCU118板卡的100G NIC工程文件。
环境准备:
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS系统(或其他linux系统)
- vivado 2020.2软件(需要破解或者激活使用)(2018.2不支持,2019.2需要修改端口代码,较为麻烦)
- 100G MAC IP LICENSE 申请地址:
- https://www.xilinx.com/products/intellectual-property/cmac_usplus.html
- https://www.xilinx.com/products/intellectual-property/cmac.html
一定要确保vivado正常功能的使用和100G MAC IP licences,否则会提示无效license导致工程恢复失败。
恢复工程:
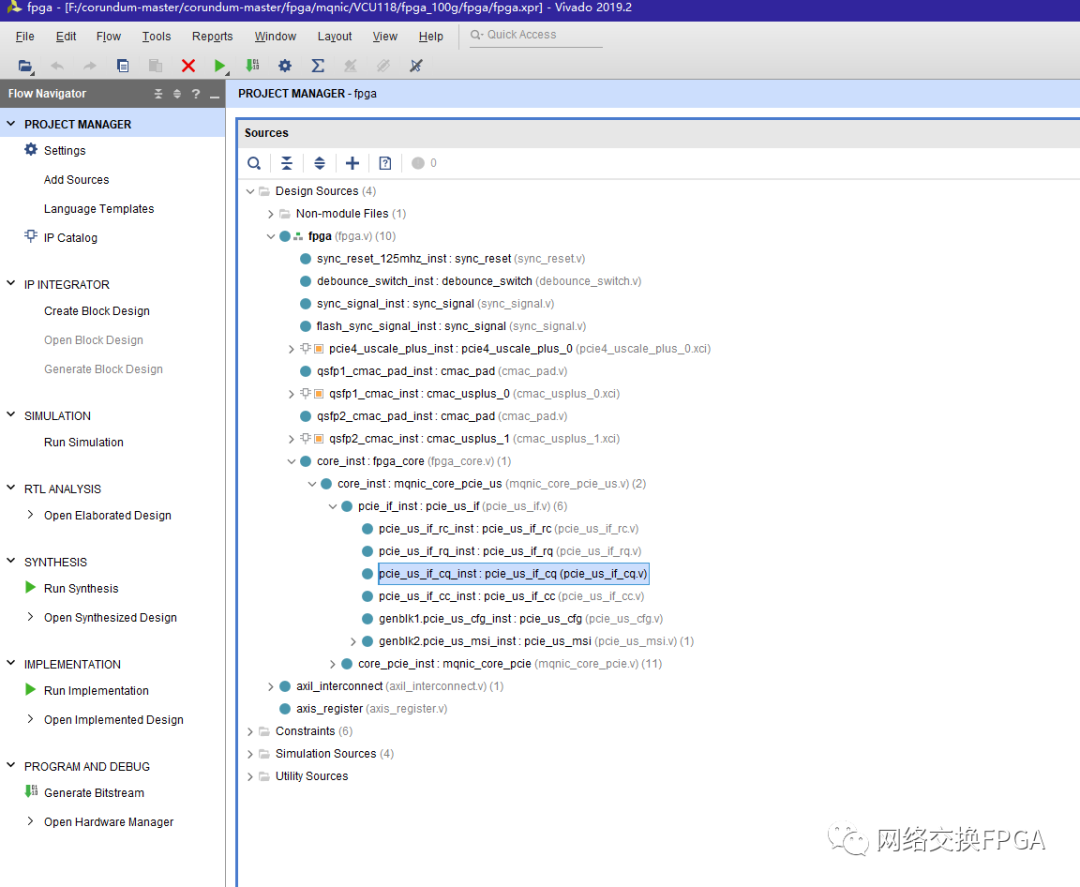
刚玉的每个设计都包含一套用于自动构建过程的makefile。要使用makefile,只需将所需工具链的设置文件源化,然后运行make。请注意,资源库大量使用了符号链接,所以强烈建议在Linux下构建设计。
$ cd /path/to/corundum/fpga/mqnic/[board]/fpga_[variant]/fpga
$ source /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2020.2/settings64.sh
$ make这里是VCU118和100G。
需要漫长的等待,运行无误便可成功恢复出工程文件。
该vivado工程文件已经将全部流程进行完毕,成功生成了bit流文件,工程文件可自行开发使用。
工程移植:
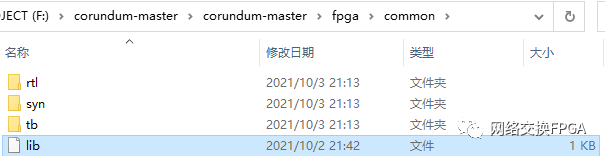
若想将恢复出来的工程移植到windows环境下使用和开发学习,请特别注意RTL文件调用时的路径。该项目资源库大量使用了符号链接,这在Linux系统下可以寻找到源文件,但这种机制在windows下不可行,因此需要将RTL文件精确调用。
类似于这个lib文件,它的内容十分简单
原创丨李钊
原文链接:网络交换FPGA
推荐阅读
更多IC设计技术干货请关注IC设计技术专栏。欢迎添加极术小姐姐微信(id:aijishu20)加入技术交流群,请备注研究方向。