背景
在微信偶然发现聆思科技的CSK6开发板的评估活动,因为经常在各种硬件平台上测试模型,因此申请了测评。很荣幸能被选中。
官方提供了开源分类的模型转换,但平常使用分类模型较少因此尝试了目标检测模型的转换。
模型架构
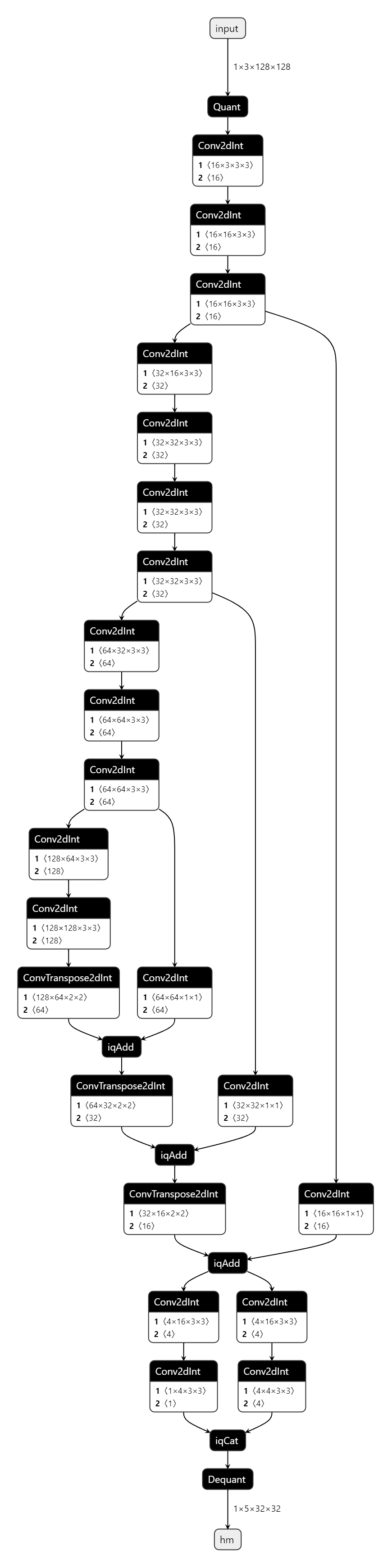
模型的思路采自centernet,基干是修改过的普通VGG块,FPN是简单的自顶向下结构,head输出了一个hm(中心点)和wh,但截至于写文章时,官方提供的烧录板子接口只能输出一个head,所以又将hm和wh cat在一起。网络结构如下
过程
环境搭建
linger与thinker 环境搭建
linger是用于量化训练的,thinker是用来转换模型的。我使用的是wsl中Ubuntu18环境。
linger配置
conda create -n linger-env python==3.7.0
conda activate linger-env
git clone https://github.com/LISTENAI/linger.git
cd linger && sh install.sh
pip -U pip
cat requirements.txt |xargs -n 1 pip install
thinker配置
conda create -n thinker-env python==3.7.0
conda activate thinker-env
git clone https://github.com/LISTENAI/thinker.git
cd thinker
bash ./scripts/x86_linux.sh
pip -U pip
cat requirements.txt |xargs -n 1 pip install
两个环境分开搭建,搭建好后我们就可以进行训练了。
模型训练及转换
模型训练过程中需要先进行浮点训练,再进行定点训练,然后再转换成.bin格式。
linger不支持tensorboard,所以要把相关代码注释掉。其余的就是添加几行代码就ok了。
原始代码
model = create_model()
model = model.to(cfg.device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), cfg.lr, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=1e-4)
修改后代码
import linger
model = create_model()
model = model.to(cfg.device)
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 128, 128,requires_grad=True).cuda()
linger.trace_layers(model, model, dummy_input, fuse_bn=True)
type_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
normalize_modules =(nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
linger.normalize_module(model, type_modules=type_modules, normalize_weight_value=16, normalize_bias_value=16,
normalize_output_value=16)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), cfg.lr, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=1e-4)
再训练完浮点模型后需要加载保存的浮点模型进行定点训练,注意需要使用更小的学习率。
import linger
model = create_model(arch=cfg.arch, num_classes=train_dataset.num_classes, inference_mode=True, onnx_flag=False)
model = model.to(cfg.device)
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 128, 128, requires_grad=True).cuda()
type_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
normalize_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
linger.normalize_module(model, type_modules=type_modules, normalize_weight_value=16, normalize_bias_value=16,
normalize_output_value=16)
model = linger.normalize_layers(model, normalize_modules=normalize_modules, normalize_weight_value=8,
normalize_bias_value=8, normalize_output_value=8)
quant_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
model = linger.init(model, quant_modules=quant_modules)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(cfg.load_model)['state_dict'])
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), cfg.lr, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=1e-4)
定点模型训练完毕后,需要转换成onnx格式
import linger
model = create_model()
model = model.to(cfg.device)
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 128, 128, requires_grad=True).cuda()
linger.SetIQTensorCat(True)
type_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
normalize_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
linger.normalize_module(model, type_modules=type_modules, normalize_weight_value=16, normalize_bias_value=16,
normalize_output_value=16)
model = linger.normalize_layers(model, normalize_modules=normalize_modules, normalize_weight_value=8,
normalize_bias_value=8, normalize_output_value=8)
quant_modules = (nn.Conv2d,nn.BatchNorm2d,nn.ConvTranspose2d)
model = linger.init(model, quant_modules=quant_modules)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(cfg.load_model)['state_dict'])
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.ones(1, 3, 128, 128).cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
torch.onnx.export(model, dummy_input, 'lnn.onnx',input_names=['input'], output_names=['hm'],
export_params=True,opset_version=12,operator_export_type=torch.onnx.OperatorExportTypes.ONNX_ATEN_FALLBACK)
模型转成onnx后需要在thinker环境中转成.bin格式
conda activate thinker-env
tpacker -g net.onnx -d True -o model.bin
如果最后一步报错,可能是因为不符合转换要求导致,按照官方要求来就行。
烧录模型到板子
首先需要安装lisa环境,这里我选择了wsl中的ubuntu22.04环境
先安装lisa zep 命令行工具,wasi-sdk,wasm-sdk,具体方式见(官网)
编译程序
配置环境变量
export WASM_THINKER_SDK="/path_to_sdk/wasm-sdk"
export WASI_TOOLCHAIN_PATH="/path_to_sdk/wasi-sdk-17.0"
安装完成后,下载官方提供的demo
lisa zep create --from-git https://cloud.listenai.com/listenai/samples/camera_image_detect.git
修改wasm 应用
cd app_wasm/
vi main.c
将文件修改为如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include "thinker/thinker.h"
static tModelHandle model_hdl;
static tExecHandle hdl;
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("BOOT: WAMR\n");
tStatus ret;
char version[30];
tGetVersion(0, version, sizeof(version));
printf("[WASM] tGetVersion: %s\n", version);
ret = tInitialize();
printf("[WASM] tInitialize: %d\n", ret);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
return 0;
}
int
set_model(void *ptr, uint32_t size)
{
tStatus ret;
uint32_t use_psram_size = 0;
uint32_t use_share_size = 0;
int num_memory = 0;
tMemory memory_list[7];
ret = tGetMemoryPlan(
memory_list, &num_memory, (int8_t *)ptr, size, &use_psram_size, &use_share_size);
printf("[WASM] tGetMemoryPlan: %d\n", ret);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
printf("[WASM] * num_memory=%d\n", num_memory);
printf("[WASM] * use_psram_size=%d\n", use_psram_size);
printf("[WASM] * use_share_size=%d\n", use_share_size);
for (int i = 0; i < num_memory; i++) {
printf("[WASM] * memory_list[%d].dev_type=%d\n", i, memory_list[i].dev_type_);
printf("[WASM] * memory_list[%d].mem_type=%d\n", i, memory_list[i].mem_type_);
printf("[WASM] * memory_list[%d].size=%d\n", i, memory_list[i].size_);
printf("[WASM] * memory_list[%d].addr=0x%08llx\n", i, memory_list[i].dptr_);
}
ret = tModelInit(&model_hdl, (int8_t *)ptr, size, memory_list, num_memory);
printf("[WASM] tModelInit: %d, model=0x%llx\n", ret, model_hdl);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
ret = tCreateExecutor(model_hdl, &hdl, memory_list, num_memory);
printf("[WASM] tCreateExecutor: %d, hdl=0x%llx\n", ret, hdl);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
return 0;
}
int
set_input(void *ptr, uint32_t size)
{
printf("[WASM] set_input(%p, %d)\n", ptr, size);
tStatus ret;
int32_t in_c = 3;
int32_t in_h = 128;
int32_t in_w = 128;
tData input;
input.dtype_ = Int8;
input.scale_ = 5;
input.shape_.ndim_ = 4;
input.shape_.dims_[0] = 1;
input.shape_.dims_[1] = in_c;
input.shape_.dims_[2] = in_h;
input.shape_.dims_[3] = in_w;
input.dptr_ = ptr;
ret = tSetInput(hdl, 0, &input);
printf("[WASM] tSetInput: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
int
get_output(void **ptr, uint32_t *size)
{
printf("[WASM] get_output\n");
tStatus ret;
ret = tForward(hdl);
printf("[WASM] tForward: %d\n", ret);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
tData output;
ret = tGetOutput(hdl, 0, &output);
printf("[WASM] tGetOutput: %d\n", ret);
if (ret != T_SUCCESS) return 1;
printf("[WASM] * output.dtype=%u\n", output.dtype_);
printf("[WASM] * output.shape.ndim=%u\n", output.shape_.ndim_);
printf("[WASM] * output.shape.ndim=%u\n", output.shape_.ndim_);
printf("[WASM] * output.dptr=0x%p\n", output.dptr_);
int shape_size = (output.dtype_ & 0xF);
for (int i = 0; i < output.shape_.ndim_; i++) {
shape_size *= output.shape_.dims_[i];
}
printf("[WASM] * shape_size=%d\n", shape_size);
*ptr = output.dptr_;
*size = shape_size;
return ret;
}
主要是修改set\_input中in\_h和in\_w为自己模型的输入输出,input.scale\_的值修改为自己模型的值,这个如何查看开源通过onnx中的input quant中的scale\_x, scale\_x=pow(2,input.scale\_)
修改主程序
cd ..
cd camera_image_detect
vi main.c
修改后的代码为
#include <zephyr/kernel.h>
#include <zephyr/device.h>
#include <zephyr/drivers/gpio.h>
#include <zephyr/drivers/video.h>
#include <zephyr/storage/flash_map.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <csk_malloc.h>
#include <lsf/services/thinker.h>
#include "lib_image.h"
#include "venus_ap.h"
#define THINKER_MODEL_ADDR (FLASH_BASE + FLASH_AREA_OFFSET(thinker_model))
double CIFAR100_TRAIN_MEAN[] = {0.5070751592371323, 0.48654887331495095, 0.4409178433670343};
double CIFAR100_TRAIN_STD[] = {0.2673342858792401, 0.2564384629170883, 0.27615047132568404};
void main(void)
{
int ret;
printk("Hello World! %s\n", CONFIG_BOARD);
/* 加载 Thinker 模型,注意传入模型的实际字节数 */
lsf_thinker_set_model((void *)THINKER_MODEL_ADDR, 421520);
const struct device *video = device_get_binding(DT_LABEL(DT_NODELABEL(dvp)));
if (video == NULL) {
printk("Video device not found\n");
return;
}
struct video_format fmt;
fmt.pixelformat = VIDEO_PIX_FMT_VYUY;
fmt.width = 640;
fmt.height = 480;
fmt.pitch = fmt.width * 2;
if (video_set_format(video, VIDEO_EP_OUT, &fmt)) {
printk("Unable to set video format\n");
return;
}
// 图像输入区域
float box[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
box[2] = fmt.width;
box[3] = fmt.height;
struct video_buffer *buffers[2];
/* Size to allocate for each buffer */
int bsize = fmt.width * fmt.height * 2;
/* Alloc video buffers and enqueue for capture */
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(buffers); i++) {
printk("#%d: Alloc video buffer: %d\n", i, bsize);
buffers[i] = video_buffer_alloc(bsize);
if (buffers[i] == NULL) {
csk_heap_info();
printk("Unable to alloc video buffer\n");
return;
}
video_enqueue(video, VIDEO_EP_OUT, buffers[i]);
}
ret = video_stream_start(video);
if (ret != 0) {
printk("Unable to start video stream\n");
return;
}
size_t result_size = 3 * 128 * 128;
size_t pixel_count = fmt.width * fmt.height;
uint8_t *result = csk_malloc(result_size); // 缩放后的图像
assert(result != NULL);
uint8_t *rgb_buffer = csk_malloc(pixel_count * 3); // 存 RGB 数组
assert(rgb_buffer != NULL);
double *input_data = csk_malloc(result_size * sizeof(double)); // 特征换算
assert(input_data != NULL);
uint8_t *final_input = csk_malloc(result_size); // 最终输入
assert(final_input != NULL);
size_t one_third_result = result_size / 3;
int8_t *output;
uint32_t output_size;
// Start process
struct video_buffer *vbuf;
ret = video_dequeue(video, VIDEO_EP_OUT, &vbuf, K_MSEC(1000));
if (ret != 0) {
printk("Video buffer dequeued failed: %d\n", ret);
return;
}
uint8_t *buffer = vbuf->buffer;
printk("Processing...\n");
vyuy_to_rgb24(buffer, rgb_buffer, pixel_count);
video_enqueue(video, VIDEO_EP_OUT, vbuf);
printk("Resizing...\n");
ImagingResample(rgb_buffer, fmt.width, fmt.height, result, 128, 128, box);
// 特征换算
printk("Feature extraction...\n");
for (int i = 0; i < result_size; i++) {
int index = i % 3;
uint8_t value = result[i];
input_data[i] = (double)(value / 255.0 - CIFAR100_TRAIN_MEAN[index]) /
CIFAR100_TRAIN_STD[index];
}
// 输入数据
printk("Input data to Thinker...\n");
for (int i = 0; i < result_size; i++) {
// final_input[i] = (int8_t)floor(input_data[i] * 64 + 0.5);
if (i < one_third_result) {
final_input[i] = (int8_t)floor(input_data[i * 3] * 64 + 0.5);
} else if (i < one_third_result * 2) {
final_input[i] = (int8_t)floor(
input_data[(i - one_third_result) * 3 + 1] * 64 + 0.5);
} else {
final_input[i] = (int8_t)floor(
input_data[(i - one_third_result) * 3 + 2] * 64 + 0.5);
}
}
// input data 给 Thinker
lsf_thinker_set_input(final_input, result_size);
// 获取 Output
lsf_thinker_get_output((void **)&output, &output_size);
int max_value = -129;
int cur_index = 0;
int xs = 0;
int ys = 0;
float score = 0;
int w = 32;
int h =32;
for (int c = 0; c < 1; c++) {
for (int h1 = 0; h1 < h; h1++) {
for (int w1 = 0; w1 < w; w1++) {
int value = output[cur_index];
if (value > max_value) {
max_value = value;
xs = w1;
ys = h1;
score = value / pow(2.0, 3);
}
cur_index++;
}
}
}
int32_t idx_lx = w * h + ys * w + xs;
int32_t idx_ty = w * h + idx_lx;
int32_t idx_rx = w * h * 2 + idx_lx;
int32_t idx_by = w * h * 3 + idx_lx;
float a1 = xs - (float)(output[idx_lx]) / pow(2.0, 3);
float b1 = ys - (float)(output[idx_ty]) / pow(2.0, 3);
float c1 = xs + (float)(output[idx_rx]) / pow(2.0, 3);
float d1 = ys + (float)(output[idx_by]) / pow(2.0, 3);
float x1 = a1 * 4 * (640.0 /128.0);
float y1 = b1 * 4* (480.0 /128.0);
float x2 = c1 * 4* (640.0 /128.0);
float y2 = d1 * 4* (480.0 /128.0);
printk("facebox:x1:%f,y1:%f,x2:%f,y2:%f,score:%f\n",x1,y1,x2,y2,score);
for (int j = 0; j < 128; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
uint8_t pixe_r = result[j * 128 * 3 + i * 3];
uint8_t pixe_g = result[j * 128 * 3 + i * 3 + 1];
uint8_t pixe_b = result[j * 128 * 3 + i * 3 + 2];
printk("\033[0;38;2;%d;%d;%dm#", pixe_r, pixe_g, pixe_b);
}
printk("\033[00m\n");
}
}
需要修改的地方为
1.double CIFAR100\_TRAIN\_MEAN[]和double CIFAR100\_TRAIN\_STD[]改为自己模型使用的值
2.lsfthinkersetmodel((void )THINKERMODELADDR, 421520)
中的第二个参数为自己模型的大小
3.resultsize = 3 128 128;改为自己模型的输入大小
4.ImagingResample(rgbbuffer, fmt.width, fmt.height, result, 128, 128, box);中的倒数第二个和第三个参数改为自己模型的输入大小
5.修改自己的后处理:将讲一下我自己的后处理逻辑:我参照的是centernet的逻辑,只不过将hm和wh两个输出cat在一起,因此最后需要拆开来看;hm为13232的特征图,wh为43232的特征图。hm代表目标中心的score值,wh代表对应中心点的左上右下的距离,组合起来就是目标框的左上和右下角点。因此先计算hm特征图,为了节省时间以及单纯认为只检测一个人脸,遍历hm特征图后得到最大值就是目标中心点,然后获取该中心点位置的wh的4个值就是目标框。
烧录到板子
1.编译wasm应用
cd app_wasm
lisa zep exec python $WASM_THINKER_SDK/cmake/sdk.py build -p .
此时会在当前目录下build文件夹中生成:thinker\_resnet18.aot
2.编译主程序
cd camera_image_detect
lisa zep build -b csk6011a_nano
此时会在当前目录下build文件夹中生成:zephyr/zephyr.bin
3.烧录到板子
lisa zep exec cskburn -s COMx -C 6 0x0 ./build/zephyr/zephyr.bin -b 748800
lisa zep exec cskburn -s COMx -C 6 0x100000 ./resource/cp.bin -b 748800
lisa zep exec cskburn -s COMx -C 6 0x200000 ./app_wasm/build/thinker_resnet18.aot -b 748800
lisa zep exec cskburn -s COMx -C 6 0x300000 ./resource/resnet18_model.bin -b 748800
其中 COMx 为 自己板子的串口,我的是COM3,需要修改对应的串口名字
./resource/resnet18\_model.bin 是自己的模型,需要修改成对应的路径
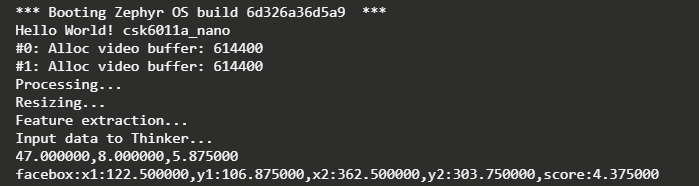
4.串口查看结果
使用官方提供的串口工具
去查看模型结果
连接板子后,按动复位键,就会看到结果