接上篇 TVM 学习指南(个人版)上
0x4. 图优化(Pass机制)
现在我们把目光转向图优化的Pass。之前我在【从零开始学深度学习编译器】七,万字长文入门TVM Pass 这篇文章中结合TVM的设计文档介绍了TVM Pass机制以及TVM编写Pass时是如何遍历节点和改写节点的,这里我们再整合一下。
首先,我们看一下TVM Pass的基类定义([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/ir/transform.h#L329](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/ir/transform.h#L329)):
`/*!
* \brief PassNode is the base type of differnt types of optimization passes.
* It is designed as a pure class and implemented by different pass subclasses
* at different granularity of Relay nodes.
*/
class PassNode : public Object {
public:
virtual ~PassNode() {}
/*!
* \brief Get the pass information/meta data. */
virtual PassInfo Info() const = 0;
/*!
* \brief Transform mod using the default PassContext in the current scope.
*
* \param mod The module that an optimization pass runs on.
*
* \return The transformed module.
*/
IRModule operator()(IRModule mod) const {
return this->operator()(std::move(mod), PassContext::Current());
}
...
};
`从operator()的定义可知,Pass做的主要是IRModule到IRModule的变换,另外这里的PassInfo和PassContext分别表示每个Pass的关键信息和多个Pass执行过程中的共同上下文信息。我们分别看一下它们的定义([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/ir/transform.h](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/ir/transform.h)):
`/*!
* \brief Meta data that will be used to help optimization and analysis.
* \sa PassInfo
*/
class PassInfoNode : public Object {
public:
/*! \brief The minimal optimization level that this pass will be enabled. */
int opt_level;
/*! \brief The name of an optimization/analysis pass. */
String name;
/*! \brief The passes that are required to perform the current pass. */
Array<String> required;
...
}
class PassContextNode : public Object {
public:
/*! \brief The default optimization level. */
int opt_level{2};
/*! \brief The list of required passes. */
Array<String> required_pass;
/*! \brief The list of disabled passes. */
Array<String> disabled_pass;
/*! \brief The diagnostic context. */
mutable Optional<DiagnosticContext> diag_ctx;
/*! \brief Pass specific configurations. */
Map<String, ObjectRef> config;
/*! \brief A list of pass instrument implementations. */
Array<instrument::PassInstrument> instruments;
...
} 这里需要注意的是在PassContextNode定义中出现了一个instrument::PassInstrument类,这个类是为开发者设计的一个工具,开发者可以实现一些函数运行在每个Pass执行前或者执行后([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/ir/transform.cc#L261](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/ir/transform.cc#L261)):
`IRModule Pass::operator()(IRModule mod, const PassContext& pass_ctx) const {
const PassNode* node = operator->();
ICHECK(node != nullptr);
const PassInfo& pass_info = node->Info();
if (!pass_ctx.InstrumentBeforePass(mod, pass_info)) {
DLOG(INFO) << "Skipping pass : " << pass_info->name
<< " with opt level: " << pass_info->opt_level;
return mod;
}
auto ret = node->operator()(std::move(mod), pass_ctx);
pass_ctx.InstrumentAfterPass(ret, pass_info);
return std::move(ret);
}
`我们可以在[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/tests/python/relay/test_pass_instrument.py](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/tests/python/relay/test_pass_instrument.py)这个测试文件中找到PassInstrument机制的示例用法, 这个功能可以方便的让我们观察每一个IRModule经过一个Pass之后变成新的IRModule之后有什么变化,方便debug或者可视化。
然后TVM为了方便实现了3个级别的Pass,即Module-Level的Pass直接操作IRModule,以及Function-Level的Pass遍历Module 中的Function进行处理,还有Sequential Pass包含一堆顺序执行的Pass(对比PyTorch的nn.Sequential)。感兴趣的读者可以自行阅读源码或者【从零开始学深度学习编译器】七,万字长文入门TVM Pass。
接下来我们讲一讲图优化Pass遍历以及重写AST节点的原理。注意,我们这里讲的Pass是TVM内置的作用于TIR AST上的Pass,我们知道TIR AST是由一系列PrimExpr和RelayExpr(非PrimExpr)来表示的,它们都继承了TVM的Expr基础类。所以TVM针对TIR AST的遍历专门做了一个工具类ExprFunctor来做,它定义在[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/relay/expr_functor.h#L67](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/relay/expr_functor.h#L67) :
`template <typename R, typename... Args>
class ExprFunctor<R(const Expr& n, Args...)> {
private:
using TSelf = ExprFunctor<R(const Expr& n, Args...)>;
using FType = tvm::NodeFunctor<R(const ObjectRef& n, TSelf* self, Args...)>;
public:
/*! \brief the result type of this functor */
using result_type = R;
/*! \brief virtual destructor */
virtual ~ExprFunctor() {}
/*!
* \brief Same as call.
* \param n The expression node.
* \param args Additional arguments.
* \return The result of the call
*/
R operator()(const Expr& n, Args... args) { return VisitExpr(n, std::forward<Args>(args)...); }
/*!
* \brief The functor call.
* \param n The expression node.
* \param args Additional arguments.
* \return The result of the call
*/
virtual R VisitExpr(const Expr& n, Args... args) {
ICHECK(n.defined()) << "Found null pointer node while traversing AST. The previous pass may "
"have generated invalid data.";
static FType vtable = InitVTable();
return vtable(n, this, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
// Functions that can be overriden by subclass
virtual R VisitExpr_(const ConstantNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const TupleNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const VarNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const GlobalVarNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const FunctionNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const CallNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const LetNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const IfNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const OpNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const TupleGetItemNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const RefCreateNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const RefReadNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const RefWriteNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const ConstructorNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExpr_(const MatchNode* op, Args... args) EXPR_FUNCTOR_DEFAULT;
virtual R VisitExprDefault_(const Object* op, Args...) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Do not have a default for " << op->GetTypeKey();
throw;
}
...
};
`
从类的定义可以看到ExprFunctor主要提供了VisitExpr函数接口,并根据Expr的具体类型转发到对应的 VisitExpr_ 。VisitExpr_ 则由派生类负责实现,当然从代码也可以看出,VisitExpr 本身也可以被重载。有了这个转发机制之后,就可以很容易的实现一个遍历所有类型Expr的类了,在TVM中叫作ExprVisitor([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/relay/expr_functor.h#L149](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/relay/expr_functor.h#L149)):
`/*!
* \brief A simple visitor wrapper around ExprFunctor.
* Recursively visit the content.
*
* ExprVisitor treats Expr as dataflow graph,
* and only visit each Expr node once.
*/
class ExprVisitor : public ::tvm::relay::ExprFunctor<void(const Expr& n)> {
public:
void VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) override;
void VisitExpr_(const VarNode* op) override;
...
protected:
// Internal visiting counter
std::unordered_map<const Object*, size_t> visit_counter_;
};
`比如对于[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/transforms/fold_constant.cc#L68](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/transforms/fold_constant.cc#L68)中的ConstantFolder这个类,就继承了ExprVisitor,并通过VisitExpr(expr),访问数据。ExprVisitor的VisitExpr成员函数实现如下([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr_functor.cc#L289](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr_functor.cc#L289)):
`void ExprVisitor::VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) {
auto it = visit_counter_.find(expr.get());
if (it != visit_counter_.end()) {
++it->second;
} else {
using TParent = ExprFunctor<void(const Expr&)>;
TParent::VisitExpr(expr);
visit_counter_.insert({expr.get(), 1});
}
}
`可以看到这个类实际上调用的是父类(ExprFunctor)的VisitExpr,而ExprFunctor的VisitExpr的实现如下:
`virtual R VisitExpr(const Expr& n, Args... args) {
ICHECK(n.defined()) << "Found null pointer node while traversing AST. The previous pass may "
"have generated invalid data.";
static FType vtable = InitVTable();
return vtable(n, this, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
`可以看到ExprFunctor设置了VisitExpr虚函数,在解析时会回到ExprVisitor来解析节点,而ConstantFolder这个类继承了ExprVisitor,这样我们只需要在ConstantFolder类中重写各个Expr节点类型的VisitExpr_函数就可以了。
在ExprFunctor的VisitExpr实现中有一个RELAY_EXPR_FUNCTOR_DISPATCH宏,这个宏的定义如下:
`#define RELAY_EXPR_FUNCTOR_DISPATCH(OP) \
vtable.template set_dispatch<OP>([](const ObjectRef& n, TSelf* self, Args... args) { \
return self->VisitExpr_(static_cast<const OP*>(n.get()), std::forward<Args>(args)...); \
});
`这里的self即为ExprFunctor的VisitExpr的实现中的vtable(n, this, std::forward<Args>(args)...),而this指向ExprFunctor。又因为ExprVisitor::VisitExpr方法调用的是ExprFunctor的函数,所以这里的this指向的是ExprVisitor实例。
以IfNode为例子,看看ExprVisitor的VisitExpr_实现。由于this指向的是ExprVisitor实例,最后会在ExprVisitor实例中生成visit_counter_的列表。
`void ExprVisitor::VisitExpr_(const IfNode* op) {
this->VisitSpan(op->span);
this->VisitExpr(op->cond);
this->VisitExpr(op->true_branch);
this->VisitExpr(op->false_branch);
}
`visit_counter_是在ExprVisitor中定义的一个unordered_map,来标记在遍历AST时某种Expr是否出现,同时记录下出现的次数来保证每个Expr都只会被访问一次。
`// Internal visiting counter
std::unordered_map<const Object*, size_t> visit_counter_;
`显然,如果AST很复杂,这样递归可能会导致Stack Overflow. 为了解决这个问题,TVM 提供了 MixedModeVisitor 来实现和 ExprVisitor 一样的功能,但是避免了 Stack Overflow。
我们上面提到对于AST除了遍历,还有改写的需求,所以TVM提供了一个ExprMutator ,同样继承了 ExprFunctor。类的定义如下:
`class ExprMutator : public ::tvm::relay::ExprFunctor<Expr(const Expr&)> {
public:
/*!
* \brief Mutate is alias for VisitExpr
* \return expr.
*/
Expr Mutate(const Expr& expr) { return this->VisitExpr(expr); }
Expr VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const VarNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const ConstantNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const GlobalVarNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const OpNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const TupleNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const FunctionNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const CallNode* call_node) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const LetNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const IfNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const TupleGetItemNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const RefCreate来表记Node* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const RefReadNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const RefWriteNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const ConstructorNode* op) override;
Expr VisitExpr_(const MatchNode* op) override;
/*!
* \brief Used to visit the types inside of expressions.
*
* Can be overloaded to transform the types in arbitrary
* ways, one way would be to define a sub-class of type
* visitor for types which transform them appropriately.
*/
virtual Type VisitType(const Type& t);
virtual Clause VisitClause(const Clause& c);
virtual Pattern VisitPattern(const Pattern& c);
protected:
/*! \brief Internal map used for memoization. */
std::unordered_map<Expr, Expr, ObjectPtrHash, ObjectPtrEqual> memo_;
};
`注意 Mutate 只是 VisitExpr 的别名。ExprMutator 的 VisitExpr 会返回一个修改后的新 Expr, 看一下 VisitExpr 的实现:
`Expr ExprMutator::VisitExpr(const Expr& expr) {
auto it = this->memo_.find(expr);
if (it != this->memo_.end()) {
return it->second;
} else {
Expr new_expr = ExprFunctor::VisitExpr(expr);
memo_[expr] = new_expr;
return new_expr;
}
}
`可以看到memo_存储了图中的各个节点。参考IfNode的实现:
`Expr ExprMutator::VisitExpr_(const IfNode* op) {
auto guard = this->Mutate(op->cond);
auto true_b = this->Mutate(op->true_branch);
auto false_b = this->Mutate(op->false_branch);
if (op->cond.same_as(guard) && op->true_branch.same_as(true_b) &&
op->false_branch.same_as(false_b)) {
return GetRef<Expr>(op);
} else {
return If(guard, true_b, false_b, op->span);
}
}
`如果IFNode的子节点都没有被修改,那么就返回这个节点本身。否则创建新的节点If(guard, true_b, false_b, op->span);并返回。这里构造新节点的类If的定义和实现分别在[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr.h](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr.h)和[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr.cc](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/relay/ir/expr.cc)中:
`class If : public Expr {
public:
/*!
* \brief The constructor
* \param cond The condition of a if node.
* \param true_branch The fall through branch
* \param false_branch The branch for execution when condition is false.
* \param span The source span of the expression.
*/
TVM_DLL If(Expr cond, Expr true_branch, Expr false_branch, Span span = Span());
TVM_DEFINE_OBJECT_REF_METHODS(If, RelayExpr, IfNode);
};
If::If(Expr cond, Expr true_branch, Expr false_branch, Span span) {
ObjectPtr<IfNode> n = make_object<IfNode>();
n->cond = std::move(cond);
n->true_branch = std::move(true_branch);
n->false_branch = std::move(false_branch);
n->span = std::move(span);
data_ = std::move(n);
`TVM的Pass里面有一个经典的算符融合Pass,之前在【从零开始学深度学习编译器】八,TVM的算符融合以及如何使用TVM Pass Infra自定义Pass 这里讲过,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看一下。
0x5. Schedule
我认为TVM的Schedule主要分为三个部分:TE Schedule,TIR Schedule以及Auto Schedule。由于精力有限我还没有探索Schedule在TVM的源码实现,不过最近TVM圈子的这篇来自Kord大佬的《TVM 自底向上(四):TE/TIR Schedule 的原理》文章为我们理清了TE/TIR Schedule的原理,个人推荐大家去阅读。链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/... 。
然后关于TE Schedule的调优以及Auto Schedule可以看一下【TVM 三代优化巡礼】在X86上将普通的矩阵乘法算子提速90倍 以及 【tvm算子优化schedule(二)--GPU篇】(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/...) 这几篇文章。
0x6. Runtime
基础概念
基础概念1: PackedFunc
为了便于Python和C++混合编程,TVM使用了统一的PackedFunc机制。PackedFunc可以将C++的函数打包成统一的函数接口并导出到Python端供用户使用,同时也支持从Python中注册一个函数,并伪装成PackedFunc在C++和Python中调用。这里推荐一篇讲解PackedFunc原理的优质博客:https://hjchen2.github.io/202... 。
基础概念2: tvm.runtime.Module
tvm.runtime.Module是tvm编译的结果(这一节之后简称Module)。Module中包含一系列可以运行的PackedFunc(所以这里的Module可以看作<name, PackedFunc>的哈希表),并且Module可以import另一个Module,从而访问其它Module的PackedFunc。我们看一下Module的接口定义([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/runtime/module.h#L47-L89](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/runtime/module.h#L47-L89)):
`/*!
* \brief Module container of TVM.
*/
class Module : public ObjectRef {
public:
Module() {}
// constructor from container.
explicit Module(ObjectPtr<Object> n) : ObjectRef(n) {}
/*!
* \brief Get packed function from current module by name.
*
* \param name The name of the function.
* \param query_imports Whether also query dependency modules.
* \return The result function.
* This function will return PackedFunc(nullptr) if function do not exist.
* \note Implemented in packed_func.cc
*/
inline PackedFunc GetFunction(const std::string& name, bool query_imports = false);
// The following functions requires link with runtime.
/*!
* \brief Import another module into this module.
* \param other The module to be imported.
*
* \note Cyclic dependency is not allowed among modules,
* An error will be thrown when cyclic dependency is detected.
*/
inline void Import(Module other);
...
};
`然后Module的具体实现由ModuleNode负责,并且不同的target对应不同的ModuleNode实现。我们来看一下CUDAModuldeNode的定义([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/runtime/cuda/cuda_module.cc#L44](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/runtime/cuda/cuda_module.cc#L44)), 请注意看下面的注释:
`// Module to support thread-safe multi-GPU execution.
// cuModule is a per-GPU module
// The runtime will contain a per-device module table
// The modules will be lazily loaded
// CUDAModuleNode对应到CUDA中的CUmodule
class CUDAModuleNode : public runtime::ModuleNode {
public:
...
// 调用cuModuleGetFunction从CUmodule中获取kernel function handle
PackedFunc GetFunction(const std::string& name, const ObjectPtr<Object>& sptr_to_self) final;
// 调用cuModuleGetGlobal从CUmodule中获取全局变量指针
CUdeviceptr GetGlobal(int device_id, const std::string& global_name, size_t expect_nbytes) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
// must recheck under the lock scope
if (module_[device_id] == nullptr) {
CUDA_DRIVER_CALL(cuModuleLoadData(&(module_[device_id]), data_.c_str()));
}
CUdeviceptr global;
size_t nbytes;
CUresult result = cuModuleGetGlobal(&global, &nbytes, module_[device_id], global_name.c_str());
ICHECK_EQ(nbytes, expect_nbytes);
if (result != CUDA_SUCCESS) {
const char* msg;
cuGetErrorName(result, &msg);
LOG(FATAL) << "CUDAError: cuModuleGetGlobal " << global_name << " failed with error: " << msg;
}
return global;
}
private:
...
std::array<CUmodule, kMaxNumGPUs> module_;
...
};
`我们看一下核心的GetFunction实现(https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/runtime/cuda/cuda_module.cc#L244-L257):
`PackedFunc CUDAModuleNode::GetFunction(const std::string& name,
const ObjectPtr<Object>& sptr_to_self) {
ICHECK_EQ(sptr_to_self.get(), this);
ICHECK_NE(name, symbol::tvm_module_main) << "Device function do not have main";
// 如果name是tvm_prepare_global_barrier,则将CUDAPrepGlobalBarrier包成一个PackedFunc返回
if (name == symbol::tvm_prepare_global_barrier) {
return PackedFunc(CUDAPrepGlobalBarrier(this, sptr_to_self));
}
auto it = fmap_.find(name);
if (it == fmap_.end()) return PackedFunc();
const FunctionInfo& info = it->second;
CUDAWrappedFunc f;
f.Init(this, sptr_to_self, name, info.arg_types.size(), info.launch_param_tags);
// 返回kernel function
return PackFuncVoidAddr(f, info.arg_types);
}
`这里首先根据函数的名称找到描述这个函数的FunctionInfo,而FunctionInfo里面包含了launch_param_tags成员,这个成员中存储了CUDA Kernel Launch时需要的gridDim/blockDim/SharedMemorySize,然后将上下文打包到CUDAWrappedFunc中并包装为一个PackFunc返回。然后我们可以看一下CUDAWrappedFunc是怎么执行的(https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/runtime/cuda/cuda_module.cc#L164-L203)。
`// invoke the function with void arguments
void operator()(TVMArgs args, TVMRetValue* rv, void** void_args) const {
int device_id;
CUDA_CALL(cudaGetDevice(&device_id));
ThreadWorkLoad wl = launch_param_config_.Extract(args);
if (fcache_[device_id] == nullptr) {
fcache_[device_id] = m_->GetFunc(device_id, func_name_);
if (wl.dyn_shmem_size >= (48 << 10)) {
// Assumption: dyn_shmem_size doesn't change across different invocations of
// fcache_[device_id]
CUresult result = cuFuncSetAttribute(
fcache_[device_id], CU_FUNC_ATTRIBUTE_MAX_DYNAMIC_SHARED_SIZE_BYTES, wl.dyn_shmem_size);
if (result != CUDA_SUCCESS) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to set the allowed dynamic shared memory size to "
<< wl.dyn_shmem_size;
}
}
}
CUstream strm = static_cast<CUstream>(CUDAThreadEntry::ThreadLocal()->stream);
CUresult result = cuLaunchKernel(fcache_[device_id], wl.grid_dim(0), wl.grid_dim(1),
wl.grid_dim(2), wl.block_dim(0), wl.block_dim(1),
wl.block_dim(2), wl.dyn_shmem_size, strm, void_args, nullptr);
if (result != CUDA_SUCCESS && result != CUDA_ERROR_DEINITIALIZED) {
const char* msg;
cuGetErrorName(result, &msg);
std::ostringstream os;
os << "CUDALaunch Error: " << msg << "\n"
<< " grid=(" << wl.grid_dim(0) << "," << wl.grid_dim(1) << "," << wl.grid_dim(2) << "), "
<< " block=(" << wl.block_dim(0) << "," << wl.block_dim(1) << "," << wl.block_dim(2)
<< ")\n";
std::string cuda = m_->GetSource("");
if (cuda.length() != 0) {
os << "// func_name=" << func_name_ << "\n"
<< "// CUDA Source\n"
<< "// -----------\n"
<< cuda;
}
LOG(FATAL) << os.str();
}
}
`
从这里可以看到CUDAWrappedFunc会根据func_name在CUDAModuleNode中找到CUfunction然后根据launch_param_config_进行Kernel Launch。这里的fcache_[device_id]是用来缓存当前device上的CUFunction的,避免重复查找带来的额外开销。另外在CUDAModuleNode::GetFunction的定义中提到如果name是tvm\_prepare_global_barrier,则将CUDAPrepGlobalBarrier包成一个PackedFunc返回,在CUDA 9.0之前是不支持Global Barrier的,所以这里TVM通过类似spin lock的方式,自旋地检查一个全局变量的值来block 线程执行,从而实现Global Barrier。核心实现见:
`class CUDAPrepGlobalBarrier {
public:
CUDAPrepGlobalBarrier(CUDAModuleNode* m, ObjectPtr<Object> sptr) : m_(m), sptr_(sptr) {
std::fill(pcache_.begin(), pcache_.end(), 0);
}
// 用一个global variable来实现GPU上的global barrier。此函数用来set global variable to 1。
// 然后kernel function中会spin的check global variable的值,为1之后,再进行接下来的操作。
// 详细看:https://github.com/apache/tvm/pull/362#issuecomment-323781410
void operator()(const TVMArgs& args, TVMRetValue* rv) const {
int device_id;
CUDA_CALL(cudaGetDevice(&device_id));
if (pcache_[device_id] == 0) {
pcache_[device_id] =
m_->GetGlobal(device_id, runtime::symbol::tvm_global_barrier_state, sizeof(unsigned));
}
CUDA_DRIVER_CALL(cuMemsetD32(pcache_[device_id], 0, 1));
}
private:
// internal module
CUDAModuleNode* m_;
// the resource holder
ObjectPtr<Object> sptr_;
// mark as mutable, to enable lazy initialization
mutable std::array<CUdeviceptr, kMaxNumGPUs> pcache_;
};
`除了CUDAModuleNode之外,其它的硬件抽象都实现了一个对应的ModuleNode比如OpenCLModuleNode,ROCMModuleNode等等。借助Module和PackFunc我们可以将不同device生成的代码打包成统一的形式。但如果想要执行这些生成的代码,我们需要做内存管理,同步等一系列操作,TVM将这些操作抽象为DeviceAPI。
基础概念3: DeviceAPI 抽象
TVM通过DeviceAPI 类来对硬件的能力进行抽象,形成了几个统一的接口(在OneFlow中有一个硬件抽象模块EP和这个类似)。只要为每一种device重载了这些统一的接口,那么执行器(runtime)就可以通过访问这些统一的接口使用device的某种能力,比如查询参数,内存分配,数据拷贝,同步等等。DeviceAPI的定义在:[https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/runtime/device_api.h#L71](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/include/tvm/runtime/device_api.h#L71)。这里有一些通用的接口比如SetDevice,GetAttr,GetTargetProperty,AllocDataSpace等等,然后对于不同的device比如cpu,cuda,hexagon,metal,rocm,vulkan,opencl都会基于各自的runtime api重写这些接口。这些接口对于TVM的执行引擎非常重要。
Module,PackFunc,DeviceAPI分别从不同的角度对硬件的功能进行了封装,比如Module封装了加载device Module(比如CUModule),加载Kernel,统一打包设备代码等功能,DeviceAPI封装了内存分配释放,数据拷贝等功能,但这些功能必须要有一个执行引擎凑到一起才可以run起来。TVM提供了2种执行引擎。
Graph Executor
GraphExecutor是TVM为静态模型设计的执行引擎(不支持动态Shape和Control Flow)。我们先看一个GraphExecutor执行一个Relay Function的示例(https://github.com/BBuf/tvm_mlir_learn/blob/main/relay/simplenet.ipynb):
`#coding=utf-8
import tvm
from tvm import relay
import numpy as np
from tvm.contrib import graph_executor
# 构造BN
def batch_norm(data,
gamma=None,
beta=None,
moving_mean=None,
moving_var=None,
**kwargs):
name = kwargs.get("name")
kwargs.pop("name")
if not gamma:
gamma = relay.var(name + "_gamma")
if not beta:
beta = relay.var(name + "_beta")
if not moving_mean:
moving_mean = relay.var(name + "_moving_mean")
if not moving_var:
moving_var = relay.var(name + "_moving_var")
return relay.nn.batch_norm(data,
gamma=gamma,
beta=beta,
moving_mean=moving_mean,
moving_var=moving_var,
**kwargs)[0]
# 构造卷积
def conv2d(data, weight=None, **kwargs):
name = kwargs.get("name")
kwargs.pop("name")
if not weight:
weight = relay.var(name + "_weight")
return relay.nn.conv2d(data, weight, **kwargs)
# 构造卷积+BN+ReLU的simpleNet
def simplenet(data, name, channels, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1), epsilon=1e-5):
conv = conv2d(
data=data,
channels=channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=strides,
padding=padding,
data_layout='NCHW',
name=name+'_conv')
bn = batch_norm(data=conv, epsilon=epsilon, name=name + '_bn')
act = relay.nn.relu(data=bn)
return act
data_shape = (1, 3, 224, 224)
kernel_shape = (32, 3, 3, 3)
dtype = "float32"
data = relay.var("data", shape=data_shape, dtype=dtype)
act = simplenet(data, "graph", 32, strides=(2, 2))
func = relay.Function(relay.analysis.free_vars(act), act)
np_data = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (1, 3, 224, 224))
params = {
"graph_conv_weight": tvm.nd.array(np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (32, 3, 3, 3)).astype(dtype)),
"graph_bn_gamma": tvm.nd.array(np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (32)).astype(dtype)),
"graph_bn_beta": tvm.nd.array(np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (32)).astype(dtype)),
"graph_bn_moving_mean": tvm.nd.array(np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (32)).astype(dtype)),
"graph_bn_moving_var": tvm.nd.array(np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (32)).astype(dtype)),
}
print(func)
with tvm.transform.PassContext(opt_level=10):
lib = relay.build(func, "llvm", params=params)
dev = tvm.cpu(0)
dtype = "float32"
m = graph_executor.GraphModule(lib["default"](dev))
# set inputs
m.set_input("data", tvm.nd.array(np_data.astype(dtype)))
# execute
m.run()
# get outputs
tvm_output = m.get_output(0)
`这里首先创建了一个GraphExecutor对象并使用Relay Function的编译结果对其进行初始化,RelayFunction的编译结果包含序列化图结构(对应executor_config)、kernel(对应mod)、weight(对应params)。
接下来为GraphExecutor对象设置输入数据,然后调用run子函数来执行kernel,最后get_output获取输出结果。GraphExecutor的实现主要有2个函数,第一个函数就是Init(https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/runtime/graph_executor/graph_executor.cc#L77)。
`/*!
* \brief Initialize the graph executor with graph and device.
* \param graph_json The execution graph.
* \param module The module containing the compiled functions for the host
* processor.
* \param devs The devices of the host and devices where graph nodes will be
* executed on.
* \param lookup_linked_param_func Linked parameter lookup function. Default is nullptr.
*/
void GraphExecutor::Init(const std::string& graph_json, tvm::runtime::Module module,
const std::vector<Device>& devs,
const PackedFunc lookup_linked_param_func) {
std::istringstream is(graph_json);
dmlc::JSONReader reader(&is);
this->Load(&reader);
module_ = module;
devices_ = devs;
lookup_linked_param_ = lookup_linked_param_func;
if (lookup_linked_param_ == nullptr) {
lookup_linked_param_ = PackedFunc(
[this](TVMArgs args, TVMRetValue* rv) { this->DefaultLookupLinkedParam(args, rv); });
}
this->SetupStorage();
this->SetupOpExecs();
for (size_t i = 0; i < input_nodes_.size(); i++) {
const uint32_t nid = input_nodes_[i];
std::string& name = nodes_[nid].name;
input_map_[name] = i;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < outputs_.size(); i++) {
const uint32_t nid = outputs_[i].node_id;
std::string& name = nodes_[nid].name;
output_map_[name] = i;
}
}
`这个函数中主要包含json参数解析。为每一个算子的input/output edge准备对应的memory(对应SetupStorage) 以及为每一个算子准备一个可调用的kernel function用来做实际的计算(对应SetupOpExecs)。
json就是计算图的表示,表示了node之间的连接关系,输入、输出node、输入shape等信息,上面的代码中Load(Read)会提取json中的信息,存储在graph_executor成员变量中。
Virtual Machine
目前我基本没有使用过这种运行时,并且了解也比较少,所以这里就留坑不展开了。VM是TVM中更加灵活的一种运行时,它可以支持动态模型(也就是带动态Shape和Control Flow的)的执行。其实,从MLC的课件也可以看到Relax在处理动态Shape程序时也用到了这个运行时。
一位Intel的工程师在《TVM Runtime System 概述》介绍了TVM的Relay Virtual Machine运行时,感兴趣的小伙伴可以去阅读一下:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/... 。
0x7. Codegen
之前提到IRModule是编译的最小单元,然后当我们执行类似于mod = tvm.build(ir_module, target="c/cuda/llvm") 可以将IRModule编译为tvm.runtime.Module,这里的target参数就是用来选择使用哪一个CodeGen来编译TIR AST的。比如我们要编译CPU可以执行的代码,那么target参数可以选择"c"或者"llvm"。如果要编译成CUDA代码,那么参数设置为"cuda"或者“llvm”。然后tvm.build会根据target参数找已经注册的build函数,在TVM中使用TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL宏注册build函数。例如:https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c_host.cc#L466 这里的TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("target.build.c").set_body_typed(BuildCHost); 以及 https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/opt/build_cuda_on.cc#L165 这里的TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("target.build.cuda").set_body_typed(BuildCUDA); 。
我们这里以生成c代码为例介绍一下Codegen的原理。当target="c"时,tvm.build调用的是提前注册的target.build.c的全局函数([https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c_host.cc#L390](https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c_host.cc#L390))。代码实现如下:
`runtime::Module BuildCHost(IRModule mod, Target target) {
using tvm::runtime::Registry;
bool output_ssa = false;
bool emit_asserts = false;
std::unordered_set<std::string> devices;
if (mod->GetAttr<Map<GlobalVar, String>>("device_contexts") != nullptr) {
Map<GlobalVar, String> device_contexts =
mod->GetAttr<Map<GlobalVar, String>>("device_contexts").value();
for (auto const& context : device_contexts) {
devices.insert(context.second.data());
}
}
// 初始化CodeGenCHost对象
CodeGenCHost cg;
cg.Init(output_ssa, emit_asserts, target->str(), devices);
cg.SetConstantsByteAlignment(target->GetAttr<Integer>("constants-byte-alignment").value_or(16));
PrimFunc aot_executor_fn;
std::vector<std::pair<tvm::GlobalVar, tvm::BaseFunc>> funcs;
for (auto kv : mod->functions) {
// Make sure that the executor function is the last one to be code generated so that all the
// symbols are available to __tvm_main__
auto fun_name = std::string(kv.first->name_hint);
bool is_aot_executor_fn = kv.second->GetAttr<Bool>("runner_function", Bool(false)).value();
if (is_aot_executor_fn) {
aot_executor_fn = Downcast<PrimFunc>(kv.second);
continue;
}
funcs.push_back(kv);
}
// Sort functions
std::sort(funcs.begin(), funcs.end(),
[](std::pair<tvm::GlobalVar, tvm::BaseFunc> kv_a,
std::pair<tvm::GlobalVar, tvm::BaseFunc> kv_b) {
std::string name_hint_a = kv_a.first->name_hint;
std::string name_hint_b = kv_b.first->name_hint;
return name_hint_a < name_hint_b;
});
// Add all functions except __tvm_main__
// 把IRModule里所有的tir::PrimFunc都放到编译列表里面
for (auto& kv : funcs) {
ICHECK(kv.second->IsInstance<PrimFuncNode>()) << "CodegenCHost: Can only take PrimFunc";
auto f = Downcast<PrimFunc>(kv.second);
cg.AddFunction(f);
}
// Add __tvm_main__
if (aot_executor_fn.defined()) {
cg.AddFunction(aot_executor_fn);
}
// NOTE: it's possible that kRuntime attr is not attached when the mod was built with tvm.build().
// See issue #10373.
auto opt_runtime = mod->GetAttr<relay::Runtime>(tvm::attr::kRuntime);
relay::Runtime runtime;
if (opt_runtime.get() != nullptr) {
runtime = opt_runtime.value();
} else {
runtime = relay::Runtime::Create("cpp", {});
}
if (aot_executor_fn.defined() && runtime->name == relay::kTvmRuntimeCpp) {
cg.InitGlobalContext();
}
if (target->GetAttr<Bool>("system-lib").value_or(Bool(false))) {
ICHECK_EQ(target->GetAttr<String>("runtime").value_or(""), "c")
<< "c target only supports generating C runtime SystemLibs";
}
// cg.Finish()是核心的函数,将IRModule Lower为c代码
std::string code = cg.Finish();
// 编译c代码并创建runtime::Module wrapper。
return CSourceModuleCreate(code, "c", cg.GetFunctionNames());
}
`上面代码中的核心是CodeGenCHost这个类,这个类定义在 https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c_host.h#L40 。这个类又继承自CodegenC类,https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c.h#L59 。我们看一下CodegenC类的定义(简化了代码):
``/*!
* \brief A base class to generate C code.
*
* CodeGenC have two modes: generate SSA formed C code or normal form.
*
* **NOTE** CodeGenC does not aim at generating C codes consumed by MSVC or GCC,
* Rather, it's providing infrastructural abstraction for C variants like CUDA
* and OpenCL-C. You might find some odd variant features, e.g., type `int3` for
* a vector of 3 `int`s. For native C code generator, see `CodeGenLLVM`.
*/
class CodeGenC : public ExprFunctor<void(const PrimExpr&, std::ostream&)>,
public StmtFunctor<void(const Stmt&)>,
public CodeGenSourceBase {
public:
/*!
* \brief Initialize the code generator.
* \param output_ssa Whether output SSA.
*/
void Init(bool output_ssa);
/*!
* \brief Add the function to the generated module.
* \param f The function to be compiled.
* \param whether to append return 0 in the end.
*/
void AddFunction(const PrimFunc& f);
/*!
* \brief Finalize the compilation and return the code.
* \return The code.
*/
std::string Finish();
/*!
* \brief Print the Stmt n to CodeGenC->stream
* \param n The statement to be printed.
*/
void PrintStmt(const Stmt& n) { VisitStmt(n); }
/*!
* \brief Print the expression n(or its ssa id if in ssa mode) into os
* \param n The expression to be printed.
* \param os The output stream
*/
void PrintExpr(const PrimExpr& n, std::ostream& os);
/*!
* \brief Same as PrintExpr, but simply returns result string
* \param n The expression to be printed.
*/
std::string PrintExpr(const PrimExpr& n) {
std::ostringstream os;
PrintExpr(n, os);
return os.str();
}
// The following parts are overloadable print operations.
/*!
* \brief Print the function header before the argument list
*
* Example: stream << "void";
*/
virtual void PrintFuncPrefix(); // NOLINT(*)
/*!
* \brief Print extra function attributes
*
* Example: __launch_bounds__(256) for CUDA functions
*/
virtual void PrintExtraAttrs(const PrimFunc& f);
/*!
* \brief Print the final return at the end the function.
*/
virtual void PrintFinalReturn(); // NOLINT(*)
/*!
* \brief Insert statement before function body.
* \param f The function to be compiled.
*/
virtual void PreFunctionBody(const PrimFunc& f) {}
/*!
* \brief Initialize codegen state for generating f.
* \param f The function to be compiled.
*/
virtual void InitFuncState(const PrimFunc& f);
// expression
void VisitExpr_(const VarNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const LoadNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const BufferLoadNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const LetNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const CallNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const AddNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const SubNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const MulNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const DivNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const ModNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const MinNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const MaxNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const EQNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const NENode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const LTNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const LENode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const GTNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const GENode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const AndNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const OrNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const CastNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const NotNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const SelectNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const RampNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const ShuffleNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const BroadcastNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const IntImmNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const FloatImmNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
void VisitExpr_(const StringImmNode* op, std::ostream& os) override; // NOLINT(*)
// statment
void VisitStmt_(const LetStmtNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const StoreNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const BufferStoreNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const ForNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const WhileNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const IfThenElseNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const AllocateNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const AttrStmtNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const AssertStmtNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const EvaluateNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const SeqStmtNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const AllocateConstNode* op) override;
void VisitStmt_(const DeclBufferNode* op) override;
...
``CodegenC类的定义中重载了VisitExpr_和VisitStmt_两种函数分别处理TIR AST中的Expression节点(表达式) 和 Statement节点(语句)。Expression(表达式)中包含了常见的变量声明、运算、判断、函数调用,而 Statement(语句)中包含了控制流(if-else,Loop 等)、内存管理、赋值等操作。在https://github.com/apache/tvm/blob/main/src/target/source/codegen_c.cc 中对每一种AST节点进行对应的代码生成(定向到一个文件输出流中),比如:
TIR AST节点一对一翻译为C代码
其它类型的Codegen比如CUDA,LLVM IR等的原理都是一样的,只不过根据target的不同AST Node翻译的目标代码语句的语法又一点区别而已。
0x8. 工具介绍
这一节为大家介绍2个有用的工具。
第一个工具是《FFI Navigator: 跨语言调用跳转IDE插件》原文见:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/103426525 。这个工具的作用就是支持tvm项目中从c++和python之间的函数调用跳转以及类型object定义的跳转。除了tvm最近小伙伴还加入了对pytorch,mxnet,dgl的支持,有兴趣的同学也可以尝试一下。可以在vscode中直接配置使用。工具的github链接:https://github.com/tqchen/ffi-navigator/
第二个工具是《Relay IR可视化》,应该也可以用到Relax上,这个工具来自一个TVM的PR(https://github.com/apache/tvm/pull/3259/files),这个PR提供了一个python/tvm/relay/visualize.py文件,我们可以稍加修改进行使用。修改后的脚本如下(注意要放到python/tvm/relay/visualize.py这个路径):
`from .expr_functor import ExprFunctor
import networkx as nx
class VisualizeExpr(ExprFunctor):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.graph = nx.DiGraph()
self.counter = 0
def viz(self, expr):
for param in expr.params:
self.visit(param)
return self.visit(expr.body)
def visit_constant(self, const): # overload this!
pass
def visit_var(self, var):
name = var.name_hint
self.graph.add_node(name)
self.graph.nodes[name]['style'] = 'filled'
self.graph.nodes[name]['fillcolor'] = 'mistyrose'
return var.name_hint
def visit_tuple_getitem(self, get_item):
tuple = self.visit(get_item.tuple_value)
# self.graph.nodes[tuple]
index = get_item.index
# import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
return tuple
def visit_call(self, call):
parents = []
for arg in call.args:
parents.append(self.visit(arg))
# assert isinstance(call.op, _expr.Op)
name = "{}({})".format(call.op.name, self.counter)
self.counter += 1
self.graph.add_node(name)
self.graph.nodes[name]['style'] = 'filled'
self.graph.nodes[name]['fillcolor'] = 'turquoise'
self.graph.nodes[name]['shape'] = 'diamond'
edges = []
for i, parent in enumerate(parents):
edges.append((parent, name, { 'label': 'arg{}'.format(i) }))
self.graph.add_edges_from(edges)
return name
def visualize(expr,mydir="relay_ir.png"):
viz_expr = VisualizeExpr()
viz_expr.viz(expr)
graph = viz_expr.graph
dotg = nx.nx_pydot.to_pydot(graph)
dotg.write_png(mydir)
`然后我们在tvm_learn/tmp/tvm/python/tvm/relay/init.py把这个visualize注册一下,添加from . import visualize 。
还需要安装一下pydot和graphviz可视化包:
`pip3 install pydot
sudo apt-get install graphviz`
最后我们就可以使用这个模块来做Relay IR的可视化了,还是以第6节的那个例子:
`#coding=utf-8
import tvm
from tvm import relay
import numpy as np
from tvm.contrib import graph_executor
from tvm.relay.visualize import visualize
# 构造BN
def batch_norm(data,
gamma=None,
beta=None,
moving_mean=None,
moving_var=None,
**kwargs):
name = kwargs.get("name")
kwargs.pop("name")
if not gamma:
gamma = relay.var(name + "_gamma")
if not beta:
beta = relay.var(name + "_beta")
if not moving_mean:
moving_mean = relay.var(name + "_moving_mean")
if not moving_var:
moving_var = relay.var(name + "_moving_var")
return relay.nn.batch_norm(data,
gamma=gamma,
beta=beta,
moving_mean=moving_mean,
moving_var=moving_var,
**kwargs)[0]
# 构造卷积
def conv2d(data, weight=None, **kwargs):
name = kwargs.get("name")
kwargs.pop("name")
if not weight:
weight = relay.var(name + "_weight")
return relay.nn.conv2d(data, weight, **kwargs)
# 构造卷积+BN+ReLU的simpleNet
def simplenet(data, name, channels, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1),
padding=(1, 1), epsilon=1e-5):
conv = conv2d(
data=data,
channels=channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
strides=strides,
padding=padding,
data_layout='NCHW',
name=name+'_conv')
bn = batch_norm(data=conv, epsilon=epsilon, name=name + '_bn')
act = relay.nn.relu(data=bn)
return act
data_shape = (1, 3, 224, 224)
kernel_shape = (32, 3, 3, 3)
dtype = "float32"
data = relay.var("data", shape=data_shape, dtype=dtype)
act = simplenet(data, "graph", 32, strides=(2, 2))
func = relay.Function(relay.analysis.free_vars(act), act)
visualize(func)
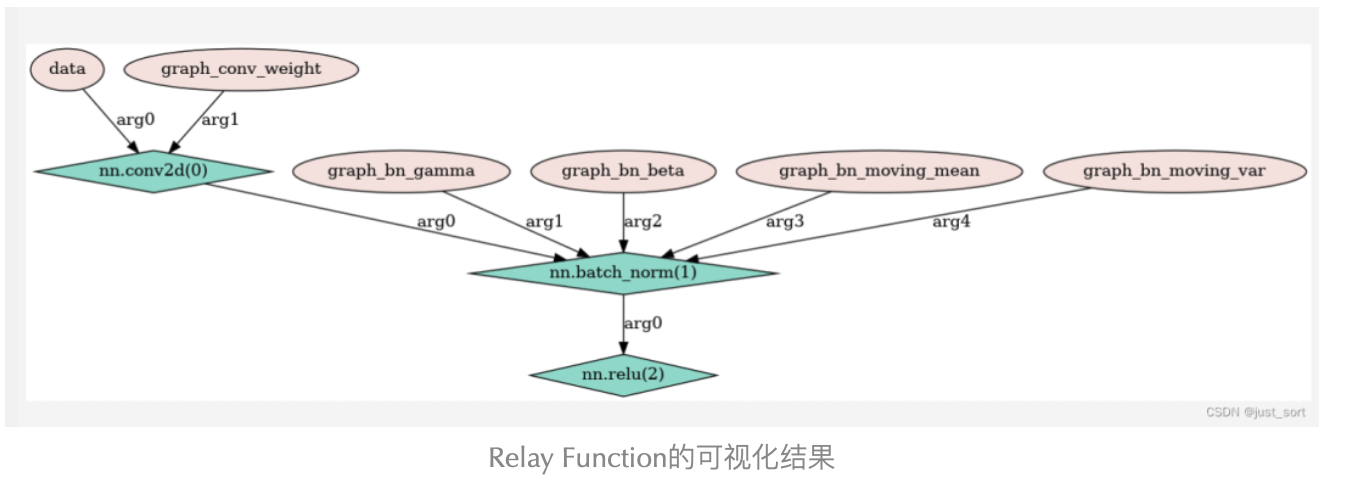
`在当前目录会生成可视化的png图片,预览一下:
我们知道TIR AST是由一系列PrimExpr和RelayExpr(非PrimExpr)来表示的,它们都继承了TVM的Expr基础类。所以TVM针对TIR AST的遍历专门做了一个工具类ExprFunctor。而这可视化个工具就是通过继承ExprFunctor来遍历计算图并自定义可视化效果。
0x9. 结论
这篇文章就是对TVM的重新梳理,从前端到图优化以及后端,比较宏观的叙述了TVM整个架构,希望对入门TVM的读者有帮助。
0x10. 参考
其它博客精选(TVM&MLIR 相关)
- 深度学习编译器 TVM 代码串讲
- TVM Overview
- TVM - Relay IR计算图可视化
- TVM - 代码生成流程
- TVM/VTA代码生成流程
- tvm算子优化schedule(一)--CPU篇
- tvm算子优化schedule(二)--GPU篇
- TVM Runtime System 概述
- TVM PackedFunc实现机制
- 向外借力:Pluto助力MLIR编译器的多面体优化
- TVM 自底向上(一):基本框架和概念
- TVM 自底向上(二):TIR 的概念和编译原理
- TVM 自底向上(三):TE 的概念和编译原理
- TVM 自底向上(四):TE/TIR Schedule 的原理
- 陈天奇 MLC课程
- 深度学习编译器学习笔记和实践体会
- FFI Navigator: 跨语言调用跳转IDE插件
作者:BBuf
文章来源: GiantPandaCV
推荐阅读
- 苹果把NeRF玩出新高度:只需单个10s视频,就能重构人物动作和场景
- 全新高性能 FPN | ssFPN 教您如何修改 FPN 让大小目标在目标检测中都有提升!!!
- 首次在智能手机上训练BERT和ResNet,能耗降35%
更多嵌入式AI干货请关注 嵌入式AI 专栏。欢迎添加极术小姐姐微信(id:aijishu20)加入技术交流群,请备注研究方向。