文章转载于:GiantPandaCV
作者:willer【GiantPandaCV导语】本文为大家介绍了一个TensorRT int8 量化部署 yolov5s 4.0 模型的教程,并开源了全部代码。主要是教你如何搭建tensorrt环境,对pytorch模型做onnx格式转换,onnx模型做tensorrt int8量化,及对量化后的模型做推理,实测在1070显卡做到了3.3ms一帧!开源地址如下:https://github.com/Wulingtian...\_tensorrt\_int8\_tools,https://github.com/Wulingtian...\_tensorrt\_int8。欢迎star。
0x0. YOLOV5简介
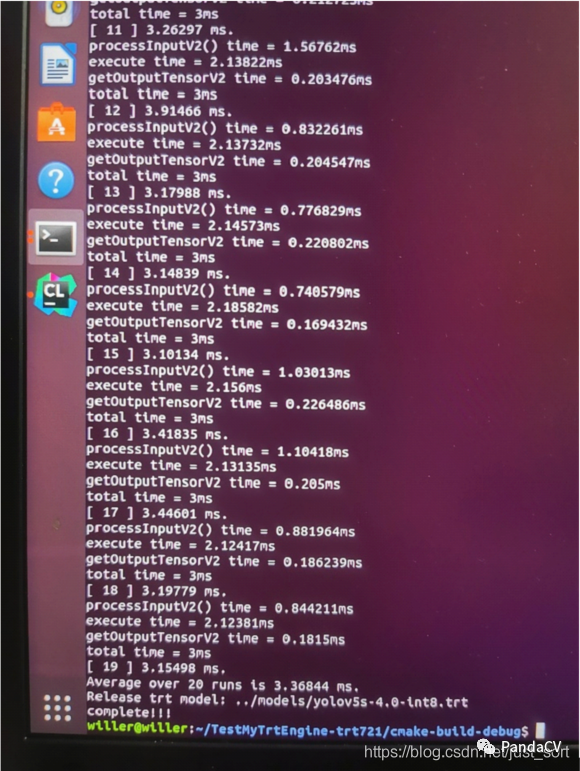
如果说在目标检测领域落地最广的算法,yolo系列当之无愧,从yolov1到现在的"yolov5",虽然yolov5这个名字饱受争议,但是阻止不了算法部署工程师对他的喜爱,因为他确实又快又好,从kaggle全球小麦检测竞赛霸榜,到star数短短不到一年突破8k,无疑,用硬实力证明了自己。总而言之,用它,用它,用它!(在我的1070显卡上,yolov5s 4.0 的模型 tensorrt int8 量化后,inference做到了3.3ms一帧!)
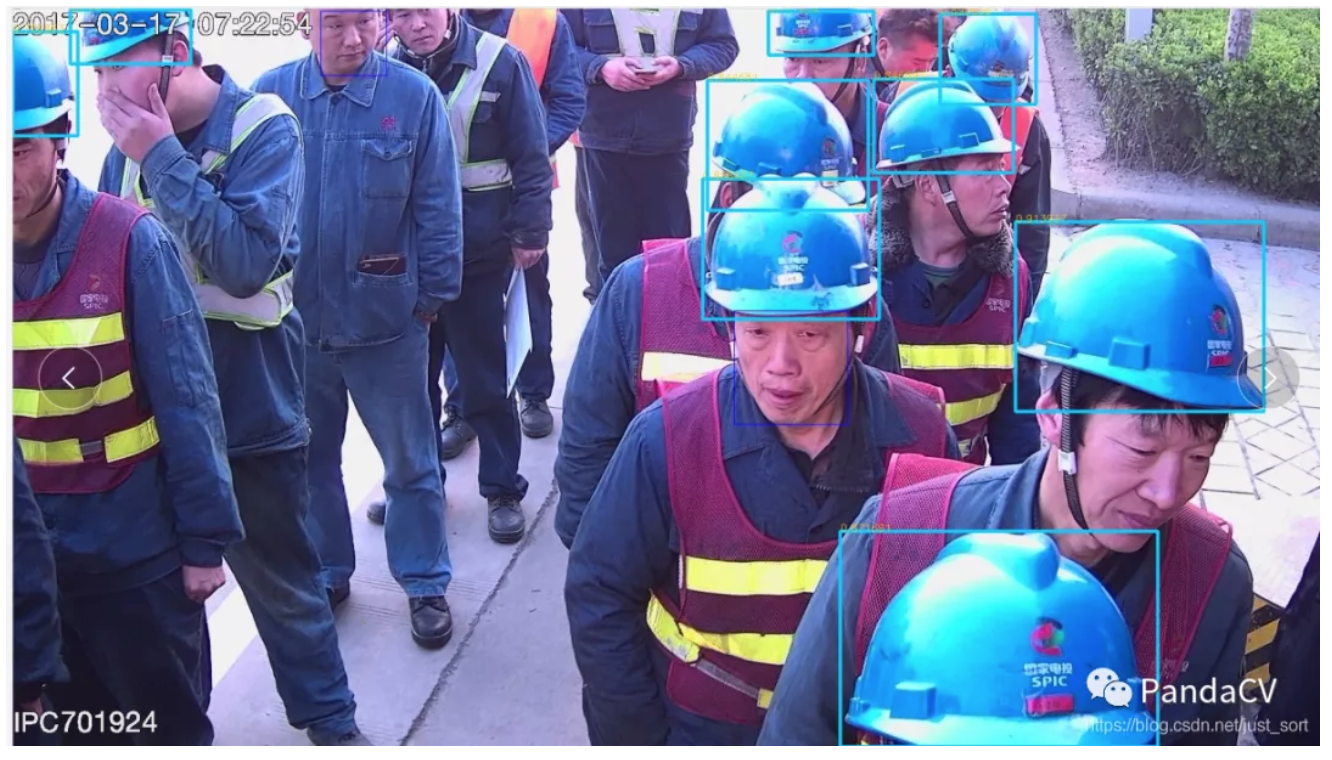
推理过程展示
0x1. 环境配置
- ubuntu:18.04
- cuda:11.0
- cudnn:8.0
- tensorrt:7.2.16
- OpenCV:3.4.2
- cuda,cudnn,tensorrt和OpenCV安装包(编译好了,也可以自己从官网下载编译)可以从链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dpMR...\_DIgGw 密码: 0rct
- cuda安装
- 如果系统有安装驱动,运行如下命令卸载
- sudo apt-get purge nvidia*
- 禁用nouveau,运行如下命令
- sudo vim /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
- 在末尾添加
blacklist nouveau - 然后执行
sudo update-initramfs -u, chmod +x cuda_11.0.2_450.51.05_linux.run,sudo ./cuda_11.0.2_450.51.05_linux.run - 是否接受协议: accept
- 然后选择Install
- 最后回车
- vim ~/.bashrc 添加如下内容:
- export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-11.0/bin:$PATH
- export LD\_LIBRARY\_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-11.0/lib64:$LD\_LIBRARY\_PATH
- source .bashrc 激活环境
- cudnn 安装
- tar -xzvf cudnn-11.0-linux-x64-v8.0.4.30.tgz
- cd cuda/include
- sudo cp *.h /usr/local/cuda-11.0/include
- cd cuda/lib64
- sudo cp libcudnn* /usr/local/cuda-11.0/lib64
- tensorrt及OpenCV安装
- 定位到用户根目录
- tar -xzvf TensorRT-7.2.1.6.Ubuntu-18.04.x86\_64-gnu.cuda-11.0.cudnn8.0.tar.gz
- cd TensorRT-7.2.1.6/python,该目录有4个python版本的tensorrt安装包
- sudo pip3 install tensorrt-7.2.1.6-cp37-none-linux\_x86\_64.whl(根据自己的python版本安装)
- pip install pycuda 安装python版本的cuda
- 定位到用户根目录
- tar -xzvf opencv-3.4.2.zip 以备推理调用
0x2. yolov5s导出onnx
- pip install onnx
- pip install onnx-simplifier
- git clone https://github.com/ultralytic...
- cd yolov5/models
- vim common.py
- 把BottleneckCSP类下的激活函数替换为relu,tensorrt对leakyRelu int8量化不稳定(这是一个深坑,大家记得避开)即修改为self.act = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
- 训练得到模型后
- cd yolov5
- python models/export.py --weights 训练得到的模型权重路径 --img-size 训练图片输入尺寸
- python3 -m onnxsim onnx模型名称 yolov5s-simple.onnx 得到最终简化后的onnx模型
0x3. ONNX模型转换为 int8 TensorRT引擎
- git clone https://github.com/Wulingtian...\_tensorrt\_int8\_tools.git(求star)
- cd yolov5\_tensorrt\_int8\_tools
- vim convert\_trt\_quant.py 修改如下参数
- BATCH\_SIZE 模型量化一次输入多少张图片
- BATCH 模型量化次数
- height width 输入图片宽和高
- CALIB\_IMG\_DIR 训练图片路径,用于量化
- onnx\_model\_path onnx模型路径
- python convert\_trt\_quant.py 量化后的模型存到models\_save目录下
0x4. TensorRT模型推理
- git clone https://github.com/Wulingtian...\_tensorrt\_int8.git(求star)
- cd yolov5\_tensorrt\_int8
- vim CMakeLists.txt
- 修改USER\_DIR参数为自己的用户根目录
- vim yolov5s\_infer.cc 修改如下参数
- output\_name1 output\_name2 output\_name3 (yolov5模型有3个输出)
- 我们可以通过netron查看模型输出名
- pip install netron 安装netron
- vim netron\_yolov5s.py 把如下内容粘贴
- import netron
- netron.start('此处填充简化后的onnx模型路径', port=3344)
- python netron\_yolov5s.py 即可查看 模型输出名
- trt\_model\_path 量化的的tensorrt推理引擎(models\_save目录下trt后缀的文件)
- test\_img 测试图片路径
- INPUT\_W INPUT\_H 输入图片宽高
- NUM\_CLASS 训练的模型有多少类
- NMS\_THRESH nms阈值
- CONF\_THRESH 置信度
- 参数配置完毕,开始编译运行
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
- ./YoloV5sEngine
- 输出平均推理时间,以及保存预测图片到当前目录下,至此,部署完成!
0x5. TensorRT int8 量化核心代码一览
//量化预处理与训练保持一致,数据对齐
def preprocess_v1(image_raw):
h, w, c = image_raw.shape
image = cv2.cvtColor(image_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Calculate widht and height and paddings
r_w = width / w
r_h = height / h
if r_h > r_w:
tw = width
th = int(r_w * h)
tx1 = tx2 = 0
ty1 = int((height - th) / 2)
ty2 = height - th - ty1
else:
tw = int(r_h * w)
th = height
tx1 = int((width - tw) / 2)
tx2 = width - tw - tx1
ty1 = ty2 = 0
# Resize the image with long side while maintaining ratio
image = cv2.resize(image, (tw, th))
# Pad the short side with (128,128,128)
image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
image, ty1, ty2, tx1, tx2, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, (128, 128, 128)
)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
# Normalize to [0,1]
image /= 255.0
# HWC to CHW format:
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
# CHW to NCHW format
#image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
# Convert the image to row-major order, also known as "C order":
#image = np.ascontiguousarray(image)
return image
//构建IInt8EntropyCalibrator量化器
class Calibrator(trt.IInt8EntropyCalibrator):
def __init__(self, stream, cache_file=""):
trt.IInt8EntropyCalibrator.__init__(self)
self.stream = stream
self.d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(self.stream.calibration_data.nbytes)
self.cache_file = cache_file
stream.reset()
def get_batch_size(self):
return self.stream.batch_size
def get_batch(self, names):
batch = self.stream.next_batch()
if not batch.size:
return None
cuda.memcpy_htod(self.d_input, batch)
return [int(self.d_input)]
def read_calibration_cache(self):
# If there is a cache, use it instead of calibrating again. Otherwise, implicitly return None.
if os.path.exists(self.cache_file):
with open(self.cache_file, "rb") as f:
logger.info("Using calibration cache to save time: {:}".format(self.cache_file))
return f.read()
def write_calibration_cache(self, cache):
with open(self.cache_file, "wb") as f:
logger.info("Caching calibration data for future use: {:}".format(self.cache_file))
f.write(cache)
//加载onnx模型,构建tensorrt engine
def get_engine(max_batch_size=1, onnx_file_path="", engine_file_path="",\
fp16_mode=False, int8_mode=False, calibration_stream=None, calibration_table_path="", save_engine=False):
"""Attempts to load a serialized engine if available, otherwise builds a new TensorRT engine and saves it."""
def build_engine(max_batch_size, save_engine):
"""Takes an ONNX file and creates a TensorRT engine to run inference with"""
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, \
builder.create_network(1) as network,\
trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER) as parser:
# parse onnx model file
if not os.path.exists(onnx_file_path):
quit('ONNX file {} not found'.format(onnx_file_path))
print('Loading ONNX file from path {}...'.format(onnx_file_path))
with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
print('Beginning ONNX file parsing')
parser.parse(model.read())
assert network.num_layers > 0, 'Failed to parse ONNX model. \
Please check if the ONNX model is compatible '
print('Completed parsing of ONNX file')
print('Building an engine from file {}; this may take a while...'.format(onnx_file_path))
# build trt engine
builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
builder.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30 # 1GB
builder.fp16_mode = fp16_mode
if int8_mode:
builder.int8_mode = int8_mode
assert calibration_stream, 'Error: a calibration_stream should be provided for int8 mode'
builder.int8_calibrator = Calibrator(calibration_stream, calibration_table_path)
print('Int8 mode enabled')
engine = builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
if engine is None:
print('Failed to create the engine')
return None
print("Completed creating the engine")
if save_engine:
with open(engine_file_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine
if os.path.exists(engine_file_path):
# If a serialized engine exists, load it instead of building a new one.
print("Reading engine from file {}".format(engine_file_path))
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) as runtime:
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
else:
return build_engine(max_batch_size, save_engine) 0x6. TensorRT inference 核心代码一览
//数据预处理和量化预处理保持一致,故不做展示
//对模型的三个输出进行解析,生成返回模型预测的bboxes信息
void postProcessParall(const int height, const int width, int scale_idx, float postThres, tensor_t * origin_output, vector<int> Strides, vector<Anchor> Anchors, vector<Bbox> *bboxes)
{
Bbox bbox;
float cx, cy, w_b, h_b, score;
int cid;
const float *ptr = (float *)origin_output->pValue;
for(unsigned long a=0; a<3; ++a){
for(unsigned long h=0; h<height; ++h){
for(unsigned long w=0; w<width; ++w){
const float *cls_ptr = ptr + 5;
cid = argmax(cls_ptr, cls_ptr+NUM_CLASS);
score = sigmoid(ptr[4]) * sigmoid(cls_ptr[cid]);
if(score>=postThres){
cx = (sigmoid(ptr[0]) * 2.f - 0.5f + static_cast<float>(w)) * static_cast<float>(Strides[scale_idx]);
cy = (sigmoid(ptr[1]) * 2.f - 0.5f + static_cast<float>(h)) * static_cast<float>(Strides[scale_idx]);
w_b = powf(sigmoid(ptr[2]) * 2.f, 2) * Anchors[scale_idx * 3 + a].width;
h_b = powf(sigmoid(ptr[3]) * 2.f, 2) * Anchors[scale_idx * 3 + a].height;
bbox.xmin = clip(cx - w_b / 2, 0.F, static_cast<float>(INPUT_W - 1));
bbox.ymin = clip(cy - h_b / 2, 0.f, static_cast<float>(INPUT_H - 1));
bbox.xmax = clip(cx + w_b / 2, 0.f, static_cast<float>(INPUT_W - 1));
bbox.ymax = clip(cy + h_b / 2, 0.f, static_cast<float>(INPUT_H - 1));
bbox.score = score;
bbox.cid = cid;
//std::cout<< "bbox.cid : " << bbox.cid << std::endl;
bboxes->push_back(bbox);
}
ptr += 5 + NUM_CLASS;
}
}
}
}
0x7. 预测结果展示
预测结果展示
预测结果展示
在我的1070显卡上,yolov5s 4.0 的模型 tensorrt int8 量化后,inference做到了3.3ms一帧!
- The End -
推荐阅读
更多嵌入式AI技术相关内容请关注嵌入式AI专栏。