转载于:GiantPandaCV
作者: BBuf
【GiantPandaCV导语】这篇文章主要是基于Relay 卷积算子和TOPI Resize算子来梳理了一下TVM的算子扭转和实现的具体过程,在这个过程中也了解到了对于不同的后端,TVM提供了各种scheduler来帮助模型加速。最后,希望看完这篇文章的读者能有所收获。其实自己看TVM算子扭转和实现的过程中对于一些小细节把握得不够,也欢迎大家和我一起讨论。(另,本人刚接触TVM,不是带佬,请不要一直知乎私信我做TVM相关的项目了,谢谢)。
0x0. 回顾
上篇文章详细的梳理了TVM的ONNX前端,我们知道了TVM是如何加载ONNX模型并将ONNX的算子转换为Relay表达式的。这篇文章我们将以卷积算子为例,来看一下Relay 表达式是如何转换为TOPI算子并结合TVM的scheduler在后端上运行的。
0x1. Relay 卷积算子的扭转过程
首先还是来到ONNX前端,我们把ONNX的卷积OP转换为TVM OP这个类贴出来:
class Conv(OnnxOpConverter):
"""Operator converter for Conv."""
@classmethod
def _impl_v1(cls, inputs, attr, params):
# Use shape of input to determine convolution type.
data = inputs[0]
input_shape = infer_shape(data)
ndim = len(input_shape)
# 处理ONNX的卷积算子属性和TVM Relay的卷积OP属性不一致的问题
kernel_type = infer_type(inputs[1])
kernel_shapes = [get_const_tuple(kernel_type.checked_type.shape)]
if "kernel_shape" not in attr:
attr["kernel_shape"] = kernel_shapes[0][2:]
if "auto_pad" in attr:
attr["auto_pad"] = attr["auto_pad"].decode("utf-8")
if attr["auto_pad"] in ("SAME_UPPER", "SAME_LOWER"):
# Warning: Convolution does not yet support dynamic shapes,
# one will need to run dynamic_to_static on this model after import
data = autopad(
data,
attr.get("strides", [1] * (ndim - 2)),
attr["kernel_shape"],
attr.get("dilations", [1] * (ndim - 2)),
ndim,
)
elif attr["auto_pad"] == "VALID":
attr["pads"] = tuple([0 for i in range(ndim - 2)])
elif attr["auto_pad"] == "NOTSET":
pass
else:
msg = 'Value {} in attribute "auto_pad" of operator Conv is invalid.'
raise tvm.error.OpAttributeInvalid(msg.format(attr["auto_pad"]))
attr.pop("auto_pad")
# 完成属性的转换以及OP转换
out = AttrCvt(
op_name=dimension_picker("conv"),
transforms={
"kernel_shape": "kernel_size",
"dilations": ("dilation", 1),
"pads": ("padding", 0),
"group": ("groups", 1),
},
custom_check=dimension_constraint(),
)([data, inputs[1]], attr, params)
use_bias = len(inputs) == 3
if use_bias:
out = _op.nn.bias_add(out, inputs[2])
return out 可以看到这个类的核心就是调用了AttrCvt函数来完成ONNX的卷积算子转换为Relay 卷积算子,这个转换包含了属性的转换以及根据layout对weights,inputs,outputs进行重排并返回一个Relay 卷积算子。AttrCvt的调用位于python/tvm/relay/frontend/common.py文件夹中,根据注释可以看到这个类主要实现了算子扭转,即根据输入的op\_name映射到Relay的算子。具体过程是,先对传入的attrs进行检查,如果有非法的属性就报错,如果属性有相应的转换策略就直接转换(即上面代码中的transforms),最后调用get_relay_op返回一个TVM Relay卷积算子。get_relay_op函数的实现如下:
def get_relay_op(op_name):
"""基于OP的名字从Relay中获得调用函数
参数
----------
op_name : str
Relay OP的名字
"""
if "." in op_name:
# explicit hierachical modules
op = _op
try:
for opn in op_name.split("."):
op = getattr(op, opn)
except AttributeError:
op = None
else:
# try search op in various modules
for candidate in (_op, _op.nn, _op.image, _op.vision, _op.contrib):
op = getattr(candidate, op_name, None)
if op is not None:
break
if not op:
raise tvm.error.OpNotImplemented("Unable to map op_name {} to relay".format(op_name))
return op 所有的op都位于python/tvm/relay/op包中,conv在op/nn中定义。上面代码中的几个for loop就是在python/tvm/relay/op下去搜寻满足OP name为op_name的Relay算子,找到就返回。至于为什么要分两种情况,这是既支持用户写module.xxx也支持直接写xxx,这里的module可以是python/tvm/relay/op包中的任何一级文件夹比如nn。nn.py中包含如下调用关系:conv2d -> _make.conv2d()。然后在_make.py中实际上实现了C++类到python类的注册,就是一行代码:
tvm._ffi._init_api("relay.op.nn._make", __name__) _init_api这个函数又实现在tvm/python/tvm/_ffi/registry.py中,具体如下:
def _init_api(namespace, target_module_name=None):
"""Initialize api for a given module name
namespace : str
The namespace of the source registry
target_module_name : str
The target module name if different from namespace
"""
target_module_name = target_module_name if target_module_name else namespace
if namespace.startswith("tvm."):
_init_api_prefix(target_module_name, namespace[4:])
else:
_init_api_prefix(target_module_name, namespace)
def _init_api_prefix(module_name, prefix):
module = sys.modules[module_name]
for name in list_global_func_names():
if not name.startswith(prefix):
continue
fname = name[len(prefix) + 1 :]
target_module = module
if fname.find(".") != -1:
continue
f = get_global_func(name)
ff = _get_api(f)
ff.__name__ = fname
ff.__doc__ = "TVM PackedFunc %s. " % fname
setattr(target_module, ff.__name__, ff) 可以看到这个函数实际上就是通过名字来获取C++注册的函数,即get_global_func会加载我们编译好的TVM动态库获取这个动态库里面的函数名称来进行匹配。获取到C++注册的函数之后就可以设置到_make.py文件中,即相当于在_make.py中定义了conv2d算子的函数了。conv2d算子的注册代码在tvm/src/relay/op/nn/convolution.cc中:
// relay.nn.conv2d
TVM_REGISTER_NODE_TYPE(Conv2DAttrs);
TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("relay.op.nn._make.conv2d")
.set_body_typed([](Expr data, Expr weight, Array<IndexExpr> strides, Array<IndexExpr> padding,
Array<IndexExpr> dilation, int groups, IndexExpr channels,
Array<IndexExpr> kernel_size, String data_layout, String kernel_layout,
String out_layout, DataType out_dtype) {
return MakeConv<Conv2DAttrs>(data, weight, strides, padding, dilation, groups, channels,
kernel_size, data_layout, kernel_layout, out_layout, out_dtype,
"nn.conv2d");
});
RELAY_REGISTER_OP("nn.conv2d")
.describe(R"code(2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
with the layer input to produce a tensor of outputs.
- **data**: This depends on the `layout` parameter. Input is 4D array of shape
(batch_size, in_channels, height, width) if `layout` is `NCHW`.
- **weight**: (channels, in_channels, kernel_size[0], kernel_size[1])
- **out**: This depends on the `layout` parameter. Output is 4D array of shape
(batch_size, channels, out_height, out_width) if `layout` is `NCHW`.
)code" TVM_ADD_FILELINE)
.set_attrs_type<Conv2DAttrs>()
.set_num_inputs(2)
.add_argument("data", "Tensor", "The input tensor.")
.add_argument("weight", "Tensor", "The weight tensor.")
.set_support_level(2)
.add_type_rel("Conv2D", Conv2DRel<Conv2DAttrs>)
.set_attr<FInferCorrectLayout>("FInferCorrectLayout", ConvInferCorrectLayout<Conv2DAttrs>);
然后我们继续跟进C++看一下卷积算子的实现,TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL这个宏定义将算子注册到一个全局对象中。可以看一下这个宏定义:
#define TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL(OpName) \
TVM_STR_CONCAT(TVM_FUNC_REG_VAR_DEF, __COUNTER__) = ::tvm::runtime::Registry::Register(OpName) 可以看到注册的实现在Registry类中,这个类有一个Register成员函数,这个函数会通过全局manager来将算子注册进去:
Registry& Registry::Register(const std::string& name, bool can_override) { // NOLINT(*)
Manager* m = Manager::Global();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m->mutex);
if (m->fmap.count(name)) {
ICHECK(can_override) << "Global PackedFunc " << name << " is already registered";
}
Registry* r = new Registry();
r->name_ = name;
m->fmap[name] = r;
return *r;
} 然后在上面的conv2d算子注册时,set_body_typed这个函数实现如下:
* \param f The function to forward to.
* \tparam FLambda The signature of the function.
*/
template <typename FLambda>
Registry& set_body_typed(FLambda f) {
using FType = typename detail::function_signature<FLambda>::FType;
return set_body(TypedPackedFunc<FType>(std::move(f), name_).packed());
} 其中set_body将通过MakeConv构建一个conv算子,然后注册到registry中。在MakeConv中,首先根据传入的conv参数,包括strides,kernel,layout等,构建atrrs对象,然后根据op的名字从已经注册过的conv算子中得到conv的算子,然后再将attrs和op一起打包到call类中。即在tvm/src/relay/op/nn/convolution_make.h中的:
template <typename T>
inline Expr MakeConv(Expr data, Expr weight, Array<IndexExpr> strides, Array<IndexExpr> padding,
Array<IndexExpr> dilation, int groups, IndexExpr channels,
Array<IndexExpr> kernel_size, std::string data_layout,
std::string kernel_layout, std::string out_layout, DataType out_dtype,
std::string op_name) {
auto attrs = make_object<T>();
attrs->strides = std::move(strides);
attrs->padding = std::move(padding);
attrs->dilation = std::move(dilation);
attrs->groups = groups;
attrs->channels = std::move(channels);
attrs->kernel_size = std::move(kernel_size);
attrs->data_layout = std::move(data_layout);
attrs->kernel_layout = std::move(kernel_layout);
attrs->out_layout = std::move(out_layout);
attrs->out_dtype = std::move(out_dtype);
const Op& op = Op::Get(op_name);
return Call(op, {data, weight}, Attrs(attrs), {});
} 这个Call类是继承了Expr类:
class Call : public Expr {
public:
/*!
* \brief The destructor
*/
~Call();
/*!
* \brief The constructor
* \param op The operator will be invoked.
* \param args The arguments of the call.
* \param attrs The attributes of the call node.
* \param type_args The type arguments passed to a polymorphic function.
* \param span The source span of the expression.
*/
TVM_DLL Call(Expr op, Array<Expr> args, Attrs attrs = Attrs(),
Array<Type> type_args = Array<Type>(), Span span = Span());
TVM_DEFINE_OBJECT_REF_METHODS(Call, RelayExpr, CallNode);
}; Op算子是通过RELAY\_REGISTER\_OP注册到一个公共AttrRegistry中的。在一个op类中实际上并没有包含这个op的计算过程,只是纳入了这个算子的输入输出以及属性的信息。
特别注意Relay OP并没有包含具体的计算过程!上面的一系列操作仅仅是拿到了Relay 卷积OP的IR以及输入和属性。那么这个OP的计算过程是在哪里完成的呢?是的,就是下面要介绍的TVM的TOPI中。
0x2. TOPI Resize算子扭转过程
TOPI是TVM自己的一个算子库,这些算子可以通过te来进行表达,可以参考官方文档:http://tvm.apache.org/docs/tu...\_primitives.html#sphx-glr-tutorials-language-schedule-primitives-py。这里以ONNX的Resize算子为例介绍一下TOPI算子在TVM中的扭转过程。首先还是定位到tvm/python/tvm/relay/frontend/onnx.py中的Resize类:
class Resize(OnnxOpConverter):
"""Operator converter for Resize"""
@classmethod
def _impl_v10(cls, inputs, attr, params):
mode = attr.get("mode").decode("ascii")
if mode == "nearest":
method = "nearest_neighbor"
elif mode == "linear":
method = "bilinear"
elif mode == "cubic":
method = "bicubic"
else:
raise tvm.error.OpAttributeInvalid(
'Value {} in attribute "mode" of operator Resize is not valid.'.format(mode)
)
scale = inputs[1]
size = _op.cast(shape_of(inputs[0]), infer_type(scale).checked_type.dtype) * scale
layout = "NCHW" # ONNX assumes NCHW layout
out_size = fold_constant(_op.strided_slice(size, [2], [4]))
return _op.image.resize(inputs[0], out_size, layout, method, "asymmetric") 可以看到这个Resize类最后调用了tvm/python/tvm/relay/op/image/image.py中的resize函数:
def resize(
data,
size,
layout="NCHW",
method="bilinear",
coordinate_transformation_mode="half_pixel",
rounding_method="",
bicubic_alpha=-0.5,
bicubic_exclude=0,
out_dtype=None,
):
"""Image resize operator.
This operator takes data as input and does 2D scaling to the given scale factor.
In the default case, where the data_layout is `NCHW`
with data of shape (n, c, h, w)
out will have a shape (n, c, size[0], size[1])
method indicates the algorithm to be used while calculating the out value
and method can be one of ("bilinear", "nearest_neighbor", "bicubic")
Parameters
----------
data : relay.Expr
The input data to the operator.
size: Tuple of Int or Expr
The out size to which the image will be resized.
layout : str, optional
Layout of the input.
method : str, optional
Scale method to used [nearest_neighbor, bilinear, bicubic].
coordinate_transformation_mode : string, optional
Describes how to transform the coordinate in the resized tensor
to the coordinate in the original tensor.
Refer to the ONNX Resize operator specification for details.
[half_pixel, align_corners, asymmetric]
rounding_method: string, optional
indicates how to find the "nearest" pixel in nearest_neighbor method
[round, floor, ceil]
bicubic_alpha: float
Spline Coefficient for Bicubic Interpolation
bicubic_exclude: int
Flag to exclude exterior of the image during bicubic interpolation
out_dtype : str, optional
Type to return. If left None returns the same type as input.
Returns
-------
result: relay.Expr
The resized result.
"""
if isinstance(size, Constant):
size = list(size.data.asnumpy().astype("int32"))
if isinstance(size, Expr):
return _dyn_make.resize(
data,
size,
layout,
method,
coordinate_transformation_mode,
rounding_method,
bicubic_alpha,
bicubic_exclude,
out_dtype,
)
return _make.resize(
data,
size,
layout,
method,
coordinate_transformation_mode,
rounding_method,
bicubic_alpha,
bicubic_exclude,
out_dtype,
) 这里又是经过了_make.resize函数,在上一节Relay 卷积算子的扭转过程中我们已经知道在_make.py中实际上实现了C++类到python类的注册,因此这里对应了TVM的TOPI Resize算子的C++算子接口。即对应了tvm/src/relay/op/image/resize.cc中的Resize OP注册代码:
TVM_REGISTER_GLOBAL("relay.op.image._make.resize").set_body_typed(MakeResize);
RELAY_REGISTER_OP("image.resize")
.describe(R"code(Perform resize to input array with nearest neighbour or bilinear interpolation.
- **data**: data is 4D array of shape
(batch_size, channels, in_height, in_width) for NCHW
(batch_size, in_height, in_width, channels) for NHWC
- **out**: Output is 4D array of shape
for layout NCHW
(batch_size, channels, size[0], size[1])
for layout NHWC
(batch_size, size[0], size[1], channels)
)code" TVM_ADD_FILELINE)
.set_attrs_type<ResizeAttrs>()
.set_num_inputs(1)
.add_argument("data", "Tensor", "The input tensor.")
.set_support_level(5)
.add_type_rel("Resize", ResizeRel)
.set_attr<TOpPattern>("TOpPattern", kInjective); 然后在TVM的CodeBase例子中这样介绍:
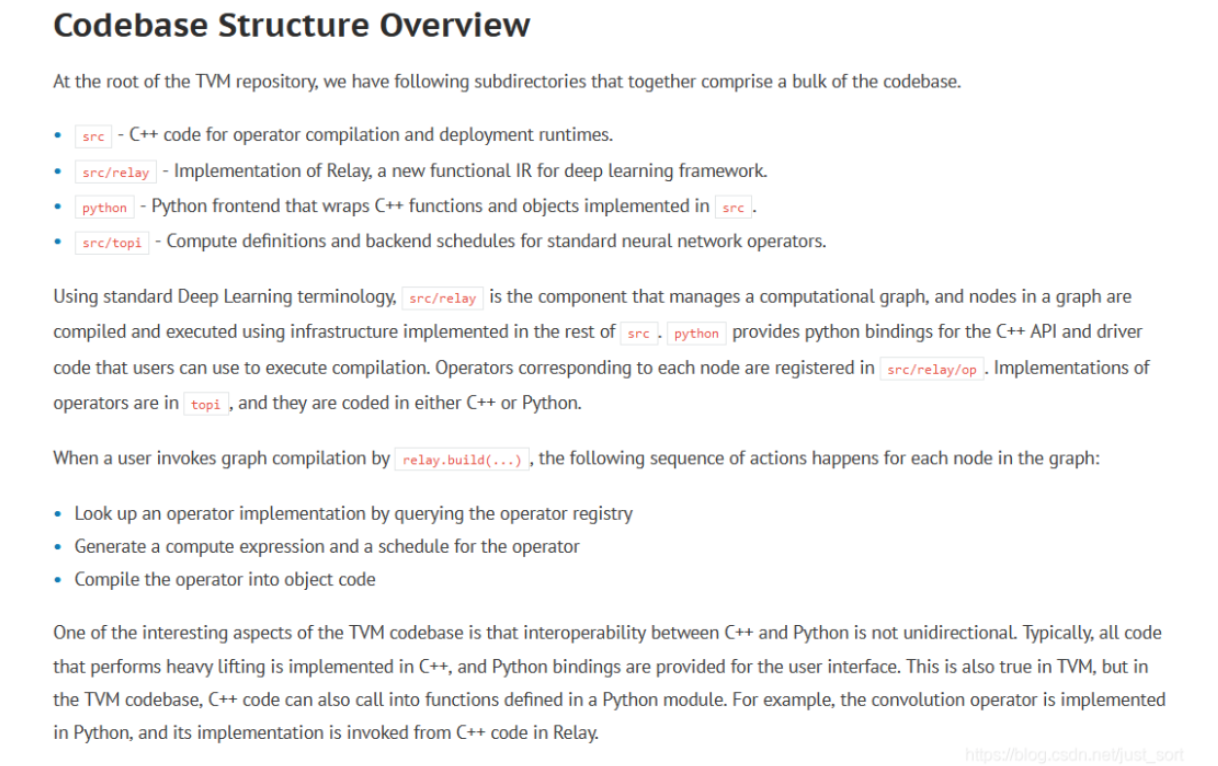
TVM CodeBase概览
最重要的一句话是,Operators corresponding to each node are registered insrc/relay/op. Implementations of operators are in topi, and they are coded in either C++ or Python.
从这里我们可以知道TVM的算子具体实现都是在tvm/python/tvm/topi这里完成的。
继续回到Resize算子,它是通过tvm/python/tvm/relay/op/image/_image.py中的下面的代码建立了OP和TOPI算子的连接:
# resize
@reg.register_compute("image.resize")
def compute_resize(attrs, inputs, out_type):
""" compute definition for resize op """
size = attrs.size
layout = attrs.layout
method = attrs.method
coord_trans = attrs.coordinate_transformation_mode
rounding_method = attrs.rounding_method
bicubic_alpha = attrs.bicubic_alpha
bicubic_exclude = attrs.bicubic_exclude
out_dtype = attrs.out_dtype
return [
topi.image.resize(
inputs[0],
size,
layout,
method,
coord_trans,
rounding_method,
bicubic_alpha,
bicubic_exclude,
out_dtype,
)
]
reg.register_injective_schedule("image.resize") 上一节的Relay nn相关的算子也有建立连接的过程,在tvm/python/tvm/relay/op/nn/_nn.py中有nn.conv2d关键字的地方。
然后我们来看一下TOPI Resize算子的具体实现代码,在tvm/python/tvm/topi/image/resize.py中的resize函数,最后一行就是根据上面传入的method来选择使用哪种插值方式进行Resize。
# Determine which interpolation method to use then run it.
if method == "nearest_neighbor":
compute_func = _nearest_neighbor
elif method == "bilinear":
compute_func = _bilinear
elif method == "bicubic":
compute_func = _bicubic
else:
raise ValueError("%s method is not supported." % method)
return te.compute(output_shape, compute_func, name="resize", tag=tag.INJECTIVE) 每个函数的具体实现方式就不细讲了,感兴趣的读者可以直接在tvm/python/tvm/topi/image/resize.py这里找到源码。
0x3. 调度
在介绍上面的TOPI算子时贴出了tvm/python/tvm/relay/op/image/_image.py中建立OP和TOPI算子的连接的代码, 其中最后一行代码如下:
reg.register_injective_schedule("image.resize") 这一行代码实际上就完成了TVM中调度的功能,我们在第二节讲过TVM中的调度是通过scheduler来完成的。【从零开始学深度学习编译器】二,TVM中的scheduler
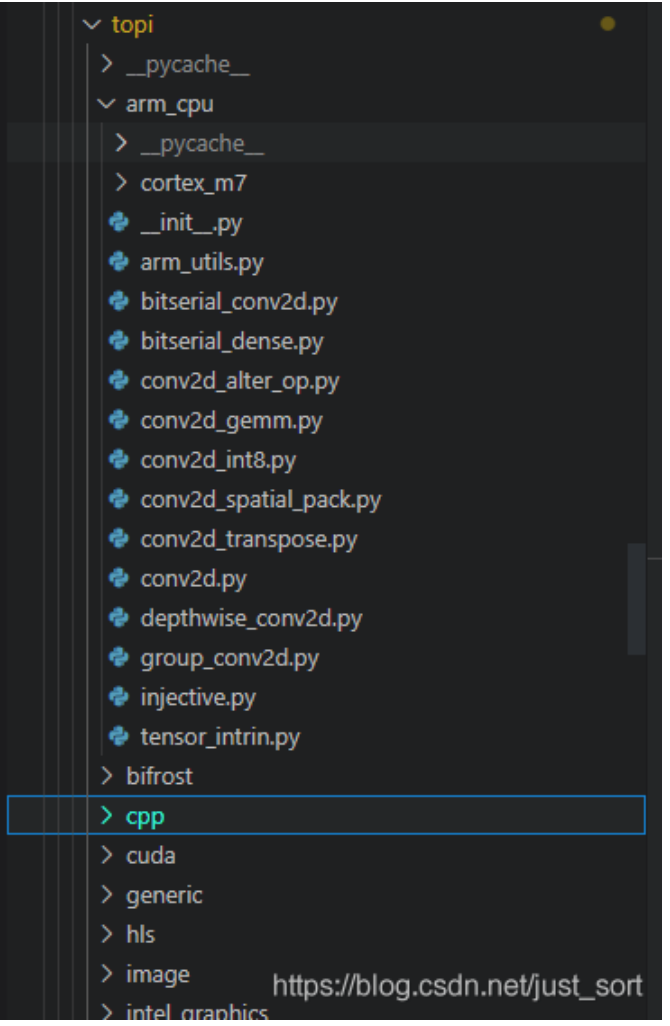
从下面的截图我们可以清楚的看到TVM对于多种硬件设备都设置了对应的scheduler
topi中对arm cpu的调度策略
对于arm\_cpu来说,卷积以及深度可分离卷积等都有特定的scheduler,而上面注册的调度方法injective是通用的scheduler,观察代码实现可以发现仅仅是做了vectorize,即下面的s[x].vectorize(ii)。
def schedule_injective(outs):
"""ARM CPU schedule for injective op.
Parameters
----------
outs: Array of Tensor
The computation graph description of injective in the format
of an array of tensors.
Returns
-------
sch: Schedule
The computation schedule for the op.
"""
outs = [outs] if isinstance(outs, te.tensor.Tensor) else outs
s = te.create_schedule([x.op for x in outs])
x = outs[0]
if list(s[x].op.axis):
# do not vectorize for broadcast
(io, ii) = s[x].split(list(s[x].op.axis)[-1], 4)
s[x].vectorize(ii)
tvm.te.schedule.AutoInlineInjective(s)
if not is_empty_shape(x.shape):
schedule_injective_from_existing(s, x)
return s 0x4. 总结
这篇文章主要是基于Relay 卷积算子和TOPI Resize算子来梳理了一下TVM中的算子扭转和实现的具体过程,在这个过程中我们也了解到了对于不同的后端,TVM提供了各种scheduler来帮助模型加速,希望看完的读者有所收获。其实自己看算子扭转和实现的过程中对于一些小细节可能还把握得不够,也欢迎大家一起讨论。
0x5. 参考
推荐阅读
更多嵌入式AI技术干货请关注嵌入式AI专栏。