转载自:知乎首先附上传送门
Problem 75 4-variable
根据卡诺图实现电路:
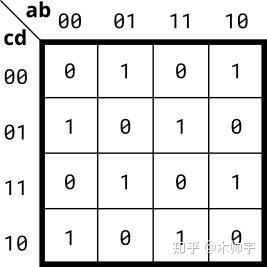
解答与解析
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
input c,
input d,
output out );
assign out = (~a&b&~c&~d) | (a&~b&~c&~d) | (~a&~b&~c&d) | (a&b&~c&d) | (~a&b&c&d) | (a&~b&c&d) | (~a&~b&c&~d) | (a&b&c&~d); //硬刚
endmodule
Problem 76 Minimum SOP and POS
一个4输入a, b, c, d和一输出的逻辑电路,当输入为2, 7或15时,输出为1, 当输入为0, 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, 或 14 时,输出为0,当输入为3,8,11或12时输出为任意值。举例来说,7对应输入abcd为0,1,1,1.
注意: 该电路的SOP和POS必须均为化简后的最小值
解答与解析:
还是根据题目已知条件画出卡诺图,然后化简得出答案,卡诺图如下所示:
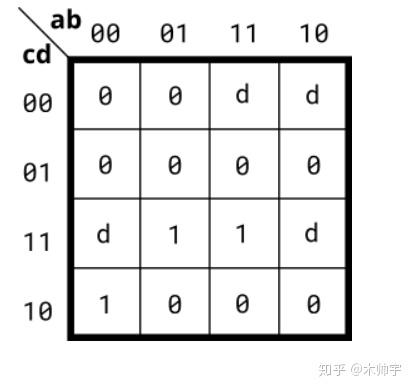
现在有一个问题就是怎么圈才是最简的?举个最小项之和的例子。
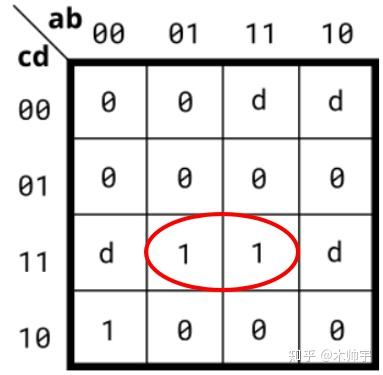
这样圈的话看似是最简: SOP = bcd;但是我们换一种方法,把D也圈在内,因为D属于don't care值

这样圈之后 SOP = ~acd + acd 化简后 SOP = cd,为最简了。
所以SOP圈法如下:
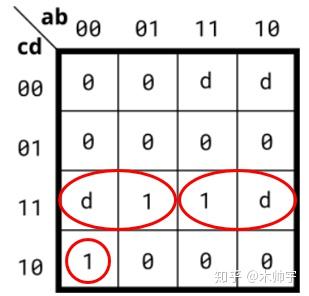
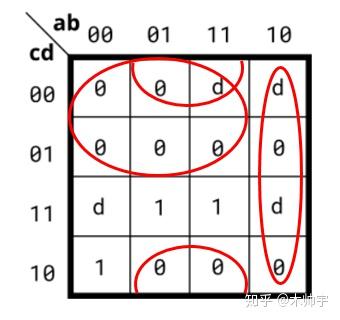
POS圈法也同上,可以将D值也圈在内来:
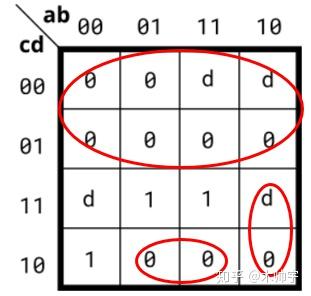
POS也可以这样圈:
代码如下
module top_module (
input a,
input b,
input c,
input d,
output out_sop,
output out_pos
);
assign out_sop = (c&d) | (~a&~b&c&~d);
assign out_pos = (c&~b&~a) | (c&d&~a) | (c&d&b);
endmodule
Problem 77 Karnaugh map
还是根据卡诺图实现电路
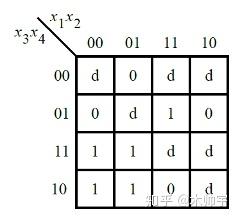
其中d还是don't care值,意味着你可以选择任何你认为方便的值。
圈法如上题,不做赘述。此处x1, x2, x3, x4 如上题a, b, c, d。
解答与解析
module top_module (
input [4:1] x,
output f );
assign f = (~x[1] & x[3]) | (x[1] & x[2] & ~x[3]);
endmodule
Problem 78 Karnaugh map
还是根据卡诺图画出电路:
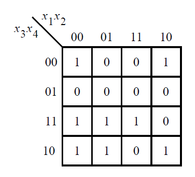
都是同理。
解答与解析
module top_module (
input [4:1] x,
output f
);
assign f = (~x[1] & x[3]) | (x[1]&x[2]&x[3]&x[4]) | (x[1] &~x[2] &~x[4]) | (~x[1] & ~x[2] & ~x[3] & ~x[4]);
endmodule
Problem 79 K-map implemented with a multiplexer
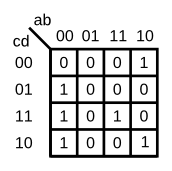
根据题目给出的卡诺图,用一个4-1的多路选择器和尽可能多的2-1多路选择器来实现电路,不允许使用其他逻辑门,必须使用ab作为选择器的输入。
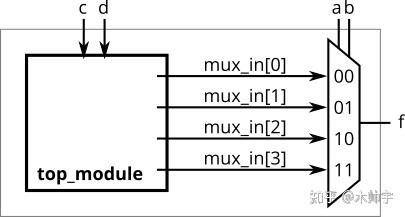
Module Declaration
module top_module (
input c,
input d,
output [3:0] mux_in
);
解答与解析
从图中所示,在ab为某一固定值的情况下,根据cd的输入不同,来选择输出。
例如当ab == 2'b00时, mux\_in[0] 根据卡诺图所示应为 c | d,
当ab == 2'b01时, mux\_in[1] 根据卡诺图所示为1'b0 ,
此处需注意mux\_in[3:0], 一个高位低位的问题,不要搞反了。
module top_module (
input c,
input d,
output [3:0] mux_in
);
assign mux_in = {(c&d),(~d),1'b0, (c|d)};
endmodule
推荐阅读
- HDLBits:在线学习 Verilog (十五 · Problem 70 - 74)
- HDLBits:在线学习 Verilog (十四 · Problem 65-69)
- HDLBits:在线学习 Verilog (十三 · Problem 60-64)
- HDLBits:在线学习 Verilog (十二 · Problem 55 - 59)
关注此系列,请关注专栏FPGA的逻辑


