这篇文章最初发表在《Electronic Design》上。
它已经正式确认!在不到一年的时间里,生成式人工智能(GenAI)已经以创纪录的速度达到了 Gartner’s Peak of Inflated Expectations。然而,今年围绕ChatGPT的讨论和新应用已经表明,GenAI不仅已经到来,而且正准备真正改变知识工作的方式。它确实是那种难得一见的变革性技术之一。我们正在看到GenAI在各个领域的应用,从电子商务网站上的实时聊天功能到软件开发中的代码生成等等。
编者注:"Gartner's Peak of Inflated Expectations" 是指Gartner公司提出的一种概念,用于描述新兴技术在其发展过程中经历的阶段。这个阶段是指当一项新技术引起广泛关注和热情时,人们对其预期过高,甚至夸大其影响和潜力。在这个阶段,人们对技术的期望往往超过了实际的成熟度和应用能力。
ChatGPT 评论道,在文章中提到的 "Generative AI has managed to reach Gartner’s Peak of Inflated Expectations" 意思是生成式人工智能已经达到了Gartner公司所描述的夸大期望的高峰。这意味着生成式人工智能在短时间内引起了广泛的关注和期望,但也需要谨慎对待,以避免过高的期望和不切实际的预期。
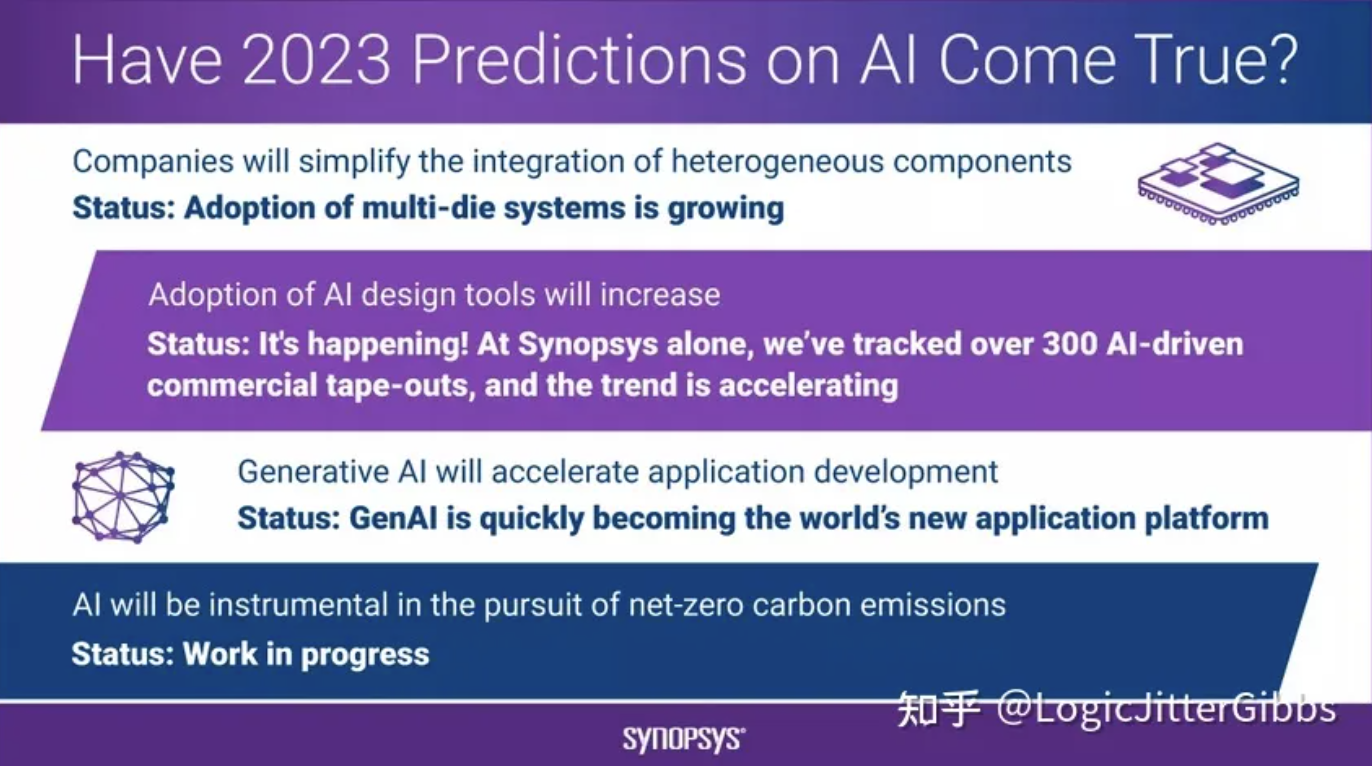
去年,当我凝视着水晶球,为2023年的人工智能做出预测时 (predictions for AI in 2023),我看到了一些正在形成的趋势(图1)。我预测公司将简化异构组件的集成(我们在多芯片系统解决方案中看到了这一点),我们将看到人工智能设计工具的日益普及(在Synopsys,我们已经追踪了300多个由AI驱动的商业项目 tapeout,并且这一趋势正在加速),生成式AI将加速应用程序开发(它正在迅速成为世界上新的应用平台),人工智能将在追求净零碳排放方面发挥重要作用(这是一个正在进行中的工作)。
图1. 这个信息图展示了我对2023年人工智能预测的结果。
2024年的人工智能前景如何?
让我们更仔细地展望一下GenAI如何塑造2024年电子行业以及随着人工智能的普及,需要解决的关键问题。
AI领航员:即将出现在您附近的设计工具中
如果您关注微软的Satya Nadella,那么您已经知道这是“ AI 领航员时代”(如果不知道,我建议观看Satya在Ignite 2023的最新主题演讲 keynote at Ignite 2023)。
编者注:ChatGPT 回答说:"Satya" 可能指的是微软公司的首席执行官萨提亚·纳德拉(Satya Nadella)。他是微软公司的领导人
半导体行业面临着一系列挑战和机遇的融合。规模和系统复杂性不断增长,而潜在的工程人才短缺威胁到创新。与此同时,供应链压力与地缘政治风险交织在一起。尽管如此,工程的创造力仍然不断带来突破,扩展了摩尔定律的优势,提高了工程生产力,并生产出了我们有史以来最复杂的电子设备和系统。
在这种背景下,GenAI在新的一年中将发挥越来越重要的作用。考虑到EDA领域非常丰富的知识领域和新人才的短缺,芯片设计 AI 领航员可以为知识共享提供高效的路径,并提高现有工程资源的生产力。例如,与其在任何给定的设计环境中停下来研究解决方案(可能需要查阅多个文档和/或联系应用工程师),不如将 AI 领航员嵌入到工具中,他可以几乎即时地回答查询。
随着2024年的推进,由GenAI驱动的领航员将在不同行业中获得更深入的立足点,我们可以预期这些领航员变得更加智能和普遍——它们将深度集成到用于设计和验证硅芯片的工作流程中。从芯片设计的角度来看,领航员的功能可以帮助工程师在几秒钟内完成以前需要数小时甚至数天才能完成的任务。
数据生态系统将开始形成
对于具有丰富设计经验的大型企业来说,GenAI具有巨大的潜力。行业领导者将部署自己的领航员,以实现几十年经验积累的方法、架构和其他领域特定数据的操作化(可以参考 NVIDIA’s ChipNeMo paper 论文,这是一个很好的例子)。与此同时,在2024年,GenAI将进一步扩大芯片设计过程的普及化,使新的硅先驱者能够比以往更快地进行创新和扩展,并专注于他们的核心价值主张,同时利用行业标准的参考流程和优化知识。
EDA公司和IP提供商将在将他们的深度专业知识、流程和IP与客户自己的领域数据相结合的过程中发挥重要作用,从而在整个技术堆栈中创建强大的GenAI解决方案。在2024年,我们可能会看到芯片设计领域形成一些早期的数据生态系统,类似于OpenAI的Sam Altman在OpenAI DevDay 2023上讨论的那些:discussed by OpenAI’s Sam Altman。这些数据合作伙伴关系将推动大规模数据集的可用性,这些数据集反映了跨多种代码、规格、寄存器传输级(RTL)、仿真等芯片设计领域的多种模态,从而使得可以为GenAI应用程序训练更好、更高效的模型成为可能。
然而,这些合作伙伴关系不会取得进展,除非新的、可扩展且安全的商业模式允许以安全且经济可行的方式共享数据。在这方面,托管微服务的出现提供了一个模式,公司将寻求探索并投入生产使用(有关深入讨论,请参阅NVIDIA最近在AWS re:Invent上的公告)。NVIDIA’s recent announcement at AWS re:Invent)。
芯片设计将变得更加以软件为中心
软件产品开发AI,例如GitHub Copilot,已经迅速获得了采用,并且在今年早些时候已经为超过46%的新代码提供支持 powering over 46% of new code as of earlier this year。半导体的硬件系统设计已经开始沿着类似以软件为中心的设计趋势发展。GenAI有潜力改变芯片设计流程,从开发设计和RTL编码,到设计验证和实现的各个步骤,最终实现系统自动化。
在微软最近的一篇关于将生成式AI引入半导体和电子设计的博客中Bringing Generative AI to Semiconductor and Electronics Design,他们详细阐述了广泛应用的敏捷软件开发实践在未来将继续影响硬件设计领域。随着半导体行业的几项能力已经变得成熟并挑战当前芯片开发的“瀑布”模型,这一趋势在2024年很可能加速发展。例如,GenAI将使得创建超快速的原型流程成为可能,为设计创作和创建带来高度自动化的选择性,并将繁琐的、细粒度的支持性开发工作(编者注:体力活)抽象化,例如验证覆盖模型、复杂断言或约束的随机测试集。
编者注:瀑布模型是一个软件生命周期模型,开发过程是通过设计一系列阶段顺序展开的,从系统需求分析开始直到产品发布和维护。每个阶段都有明确的目标和交付成果。这种模型的特点是各个阶段之间是线性顺序的,即前一个阶段的输出作为下一个阶段的输入,类似于瀑布一样一级级向下流淌,因此得名瀑布模型。
比如一个来自 ChatGPT 的例子:
假设一个团队正在开发一款新型的移动处理器芯片,他们选择使用瀑布模型进行芯片设计和开发。以下是该项目在瀑布模型下的具体实施过程:
- 需求分析阶段:团队与客户(可能是手机制造商)沟通,了解客户对移动处理器的需求。他们确定了处理器的性能要求、功耗限制、支持的功能等。
- 架构设计阶段:根据客户需求,团队设计了处理器的整体架构,包括处理器核心数量、缓存结构、指令集架构等。
- 逻辑设计阶段:在架构设计完成后,团队进行逻辑设计,将处理器的功能划分为各个模块,并设计各个模块的逻辑电路。
- 物理设计阶段:完成逻辑设计后,团队进行物理设计,包括布局设计、时序优化、功耗优化等,以确保芯片的性能和功耗符合要求。
- 验证阶段:经过物理设计后,芯片会进行各种验证,包括功能验证、时序验证、功耗验证等,以确保芯片设计的正确性和稳定性。
- 生产阶段:验证通过后,芯片会进入生产阶段,进行芯片的制造和测试,最终投入市场供应手机制造商使用。
AI经济壁垒将推动更多AI硬件创新
众所周知,当今的AI工作负载具有高度的计算密集性。特别是预训练大型语言模型(LLM)需要访问供应紧张的AIs超级计算系统和芯片。随着神经网络中参数的数量继续呈指数级增长(据估计,每两年增长超过200倍over 200x every 2 years),AI的经济“壁垒”正在变得非常明显。CPU、GPU、xPU和系统集成领域的先驱者正在加大对能够提供更多能源经济性和总拥有成本优势的架构的投资,以扩大AI时代。
在2024年,我们将继续看到新的AI处理架构的推出,包括备受期待的神经形态计算设备、光学甚至量子计算机,它们有望将AI的经济壁垒推向未来。这些异构计算元素的集成将加强行业向多芯片系统的转变,并将与A尺寸(0.1nm)CMOS器件的持续强劲推动相辅相成。虽然这些计算设备将主要针对数据中心,但边缘侧也会继续将非常重要的计算能力整合到自动驾驶车辆、工业应用和个人计算解决方案中,边缘测的创新重点将在传感器集成上。
负责任地使用AI将在芯片设计中开辟新的道路
GenAI以我们从未见过的方式实现了数据的可操作化。事实上,这在很大程度上是由于数字世界中数据的大量增加所造成的。AI领域的一些思想领袖警告说,GenAI的创新可能超过了我们理解其影响并应对其后果的能力。
在2024年,数据隐私和治理将得到深入探讨。工业界和政府已经就AI对可持续性、社会和商业的影响以及其伦理考虑进行了许多讨论。例如,最近发布的NIST AI风险管理框架 NIST AI Risk Management Framework为AI产品开发提供了重要工具。随着AI在我们的世界中越来越深入,出现监管框架以提供指导和保护措施也不足为奇。
负责任的使用可能听起来像是一种限制,但实际上它是一种必要的前提条件。在我最近在硅谷领导力集团2023年度会议上的主题演讲中Silicon Valley Leadership Group Retreat 2023,我探讨了将AI在芯片设计中的角色从今天的“告知-询问”、低信任交互提升到潜在未来的“共享-发现”或共同创造问题解决网络的路径。为了发挥其全部潜力,并在人类创造者中赢得一席之地,AI需要展示公平性、可靠性、隐私性、包容性、透明度、问责性——换句话说,所有负责任使用的要素。
新的一年,新的创新
创新是一种与生俱来的人类特质,然而AI已经展示了它如何增强和加速我们的能力。随着时间的推移,它甚至可能赢得我们的信任。在2024年,我们应该思考与AI的互动以及如何与其合作。虽然我们人类继续推动独特的想法,但AI可以作为我们的共同创作者,帮助我们实现比以往更多的成就。未来比我们想象的更近。
关于作者
Stelios Diamantidis
Stelios Diamantidis自2017年开始领导Synopsys的人工智能技术战略,目前担任中央生成式人工智能卓越中心的负责人。他将最新的基础模型技术应用于解决集成系统设计和制造中的系统复杂性问题。在2020年,Stelios推出了DSO.ai™,这是世界上第一个用于芯片设计的自主人工智能应用程序。DSO.ai是一项真正具有变革性的技术,已被全球前十大半导体公司中的9家采用,并随后推出了Synopsys.ai,这是全球第一个由人工智能驱动的全套EDA套件。Stelios在系统、半导体和EDA软件领域拥有超过20年的经验。作为一名充满激情的技术专家,他开创了几项EDA应用,包括设计验证IP(2001年)、受限随机度量驱动验证(2003年)、设计测试(DFT)验证(2005年)和速度匹配后硅验证(2007年)。Stelios还领导了几项行业标准,包括IEEE1647(标准功能验证语言副主席)和IEEE1687(创始成员,仪器访问和控制标准)。Stelios发表了大量关于半导体设计和测试的论文和文章,并经常在行业会议和活动中发表演讲。他是IEEE的会员,拥有斯坦福大学电气工程硕士学位。
原文:Generative AI to Usher in Big Opportunities in 2024
Stelios Diamantidis Feb 08, 2024
This article was originally published on Electronic Design.
It’s official! In less than a year, Generative AI has managed to reach Gartner’s Peak of Inflated Expectations, likely in record time. Yet, all the talk and new applications around ChatGPT this year have demonstrated that GenAI is not only here to stay, but it is poised to truly alter the way knowledge work is done. It is, indeed, one of those transformative technologies that only comes about once in a blue moon. We’re seeing examples of GenAI in action in everything from real-time chat functions on e-commerce sites to code generation in software development and much more.
Last year, when I peered into my crystal ball to highlight predictions for AI in 2023, I saw a number of trends taking shape (Figure 1). I predicted that companies would simplify the integration of heterogeneous components (which we’re seeing in solutions for multi-die systems), that we’d see growing adoption of AI design tools (at Synopsys we’ve tracked over 300 AI-driven commercial tapeouts, and the trend is accelerating), that generative AI would accelerate application development (it’s quickly becoming the world’s new application platform), and that AI would be instrumental in the pursuit of net zero carbon emissions (this is a work in progress).
Figure 1. This infographic highlights the outcomes of my 2023 AI predictions.
What’s on tap for AI in 2024?
Let’s take a closer look ahead at how GenAI might shape the electronics industry in 2024 and the key considerations that will need to be addressed as AI becomes more prevalent.
AI Copilots: Coming to a Design Tool Near You
If you follow Microsoft’s Satya Nadella, then you already know this is “The Era of Copilots” (if not, I recommend watching Satya’s recent keynote at Ignite 2023).
The semiconductor industry is facing a convergence of challenges and opportunities. Scale and systemic complexities continue to grow, while a looming engineering talent shortage threatens to stifle innovation. At the same time, supply chain pressures intertwined with geo-political headwinds persist. Still, engineering ingenuity continues to deliver breakthroughs that are extending the advantages of Moore’s law, enhancing engineering productivity, and, ultimately, producing some of the most sophisticated electronic devices and systems we’ve ever had.
Against this backdrop, GenAI figures to play an increasingly prominent role in the new year. Considering the very rich knowledge domain that is EDA, and the short supply of new talent to complement deep experience, chip design copilots can provide an efficient path for knowledge-sharing and enhance productivity of existing engineering resources. For example, rather than having to pause to research solutions in any given design context—potentially wading through multiple documents and/or contacting an applications engineer—a copilot embedded into a tool could deliver responses to queries almost instantaneously.
As 2024 progresses and GenAI-driven copilots gain a deeper foothold across different industries, we can expect to see these copilots becoming smarter and ubiquitous–being deeply integrated into the workflows used to design and verify silicon chips. From a chip design perspective, copilot capabilities could help engineers do things in seconds that previously required hours or even days.
Data Ecosystems Will Begin to Take Shape
GenAI holds tremendous promise for large, established companies with deep design expertise. Industry leaders will deploy their own copilots to operationalize treasure troves of methodology, architecture, and other domain-specific data accumulated over decades of experience (check out NVIDIA’s ChipNeMo paper for an excellent example). At the same time, in 2024, GenAI will further expand democratization of the chip design process, allowing new silicon pioneers to innovate and scale faster than ever before, and to focus on their core value proposition while tapping into industry-standard reference flows and optimization knowledge.
EDA companies and IP providers will play an important role in bringing together their deep expertise, flows, and IP with customers’ own domain data to create powerful GenAI solutions across the entire technology stack. In 2024, we will likely see the formation of some early data ecosystems in chip design, similar to the ones discussed by OpenAI’s Sam Altman at OpenAI DevDay 2023. These data partnerships will drive the availability of large-scale data sets that reflect chip design domains across multiple modalities of code, specs, register-transfer level (RTL), simulations, etc., making it possible to train better, more efficient models for GenAI applications.
These partnerships, however, will not take flight unless new, scalable, and secure business models allow sharing of data in a secure and economically viable manner. Here, the emergence of hosted micro-services offers a model that companies will look to explore and put into production use (for a good discussion, see NVIDIA’s recent announcement at AWS re:Invent).
Chip Design Will Become Even More Software-Centric
Software product development AI, such as GitHub Copilot, has gained rapid adoption and was powering over 46% of new code as of earlier this year. Hardware systems design for semiconductors has already started to evolve along a similar software-centric design trend. GenAI has the potential to transform the chip design flow, from design authoring and RTL, through the various steps in design verification and implementation, leading towards systems automation.
In an engaging blog on Bringing Generative AI to Semiconductor and Electronics Design, Microsoft recently outlined how pervasive, agile software development practices are likely to continue to influence the hardware design world. This trend will more than likely pick up pace in 2024, as several capabilities in the semiconductor industry are already becoming mature and are challenging the current “waterfall” model for chip design. For example, GenAI will make it possible to create ultra-fast prototyping flows, bringing highly automated optionality to design authoring and creation, and abstracting away the labor-intensive, fine-grain development of supporting collateral, such as verification coverage models, complex assertions, or constrained-random test stubs.
The AI Economic Wall Will Drive More AI Hardware Innovation
It is no secret that today’s AI workloads are highly computationally intensive. Pre-training large language models (LLMs), in particular, requires access to AI supercomputing systems and silicon chips that are in very high demand. As the number of parameters in neural networks continues to grow exponentially (per one estimate, over 200x every 2 years), the upcoming economic “wall” for AI is becoming very clear. Pioneers across the CPU, GPU, xPU, and system integration worlds are intensifying investments in architectures that offer energy-consumption and total-cost-of-ownership benefits to expand the era of AI.
In 2024 we will continue to see the debut of new AI processing architectures, including much-anticipated neuromorphic computing devices, optical, and even quantum computers that hold the promise of pushing the AI economic wall further out in the future. The integration of these heterogeneous compute elements will amplify the industry’s move towards multi-die systems and will complement the continued strong push towards angstrom-scale digital CMOS devices. While these compute devices will be targeting the data center, the autonomous edge will continue to integrate very significant compute power into autonomous vehicles, industrial applications, and personal computing solutions, where the innovation focus will be placed on sensor integration.
Responsible Use of AI Will Open New Paths in Chip Design
GenAI operationalizes data in a way that we’ve never seen before. In fact, it is made possible in large part due to the proliferation of data in our digital world. Several thought leaders in the AI space have warned that GenAI innovation may be outpacing our ability to make sense its implications and respond to its consequences.
In 2024, data privacy and governance will be explored deeply. There already are many discussions in industry and government around AI’s impact on sustainability, society, and business, as well as its ethical considerations. For example, the recently published NIST AI Risk Management Framework offers an important tool for AI product development. As AI becomes increasingly ingrained in our world, the emergence of regulatory frameworks to provide guidelines and protections would not be surprising.
Responsible use may sound like a restriction; however, it is instead an essential precondition. In my recent keynote at the Silicon Valley Leadership Group Retreat 2023, I explored the path forward for elevating the role of AI in chip design from today’s “tell-ask,” low-trust interactions to potential future “share-discover,” or co-creator, problem-solving networks. To reach its full potential, and earn its place among human creators, AI will need to demonstrate fairness, reliability, privacy, inclusiveness, transparency, accountability – in other words, all the elements of responsible use.
New Year, New Innovations
Innovation is an inherently human trait, yet AI is already demonstrating how it can augment and accelerate our abilities. In time, it may even win our trust. In 2024, we should think about our interaction with AI and how we can collaborate with it. While we humans continue to drive unique ideas, AI can act as our co-creator, helping us accomplish more than ever before. The future is closer than we think.
Stelios Diamantidis
Stelios has been leading Synopsys’ AI technology strategy since the inception of the program in 2017. He is currently the head of the central Generative AI Center of Excellence, where he applies latest foundation model technologies to address systemic complexity in the design and manufacturing of integrated systems. In 2020, Stelios launched DSO.ai™, the world’s first autonomous AI application for chip design. A truly transformative technology, DSO.ai has been adopted by 9 of the top-10 semiconductor companies worldwide and was followed by Synopsys.ai, the world’s first AI-driven full-stack EDA suite. Stelios has more than 20 years of experience in systems, semiconductors, and EDA software. A passionate technologist, he has pioneered several EDA applications including design verification IP (2001), constrained-random metric-driven verification (2003), design-for-test (DFT) verification (2005), and at-speed post-silicon validation (2007). Stelios has also led several industry standards including IEEE1647 (vice chair, Standard for Functional Verification Language) and IEEE1687 (founding member, Standard for Access and Control of Instrumentation). Stelios has published numerous papers and articles on the design and test of semiconductors and routinely presents at industry conferences and events. He is a Member of the IEEE and holds an M.S. degree in electrical engineering from Stanford University.
原文:知乎
作者:LogicJitterGibbs
相关文章推荐
- Synopsys DDR 相关技术白皮书与 IP 技术公告合集
- 翻译 Micron DDR TN-46-15: 低功耗与标准 DDR SDRAM 对比
- 【译文】 芯片设计后端知识笔记: Minimum Pulse Width 检查
- 【译文】芯片设计后端知识笔记: Useful Skew 介绍
- DDR 学习时间 (Part C - 3): DFI PHY 与 DFI 时钟频率比
更多FPGA干货请关注FPGA的逻辑技术专栏。欢迎添加极术小姐姐微信(id:aijishu20)加入技术交流群,请备注研究方向。